Cyber Security | Types, Definition, Protection and Safety
Cyber Security|Safety| Types, Definition and Protection
Introduction – : Are you CBSE Board student? And you have Computer Science as a subject in you CBSE Class Curriculum/Syllabus! This tutorial is surely for you.
This Cyber Security and Safety tutorial will help you to learn Cyber and Internet Security or Safety basics and concepts like Definition,Types,Protections etc and no doubt, you will be able to score highest marks in you CBSE class 11th and 12th.
This tutorial will help you to fulfill all the CBSE Board academic requirements of a student who has computer science as a subject in CBSE schools in India as well as outside India.
This tutorial covers all necessary topics/concepts required to complete your exams preparations in CBSE schools / classes.
After 10 years of CBSE school teaching and experience, we have prepared this school study tutorial.Our expert team have had a lot of research and finally designed these study material for CBSE Board exams preparation.
All study material is freely available for students.
Let’s Get Start!
Cyber Safety | Internet Safety
Today’ s age cannot be even thought of without Internet, even in dreams. Although Internet has made many things easier but at the same time it has posed many security risks too, if not used in a proper way. Thus, it is important to know about possible threats, challenges and risks of working on Internet to ensure personal safety and information security. This topic deals with nearly all important concepts required in CBSE Class 11th syllabus & examinations. It talks about possible risks and threats on Internet and the safety measures to avoid them.
What is Cyber Safety ?
Cyber Safety refers to the safe and responsible use of Internet So as to ensure safety and security of personal information and not posing threat to anyone else’s information. It involves gaining knowledge about possible threats to personal safety and security risks for the information along with measures to prevent and counter them.
Safely Browsing the web | Internet
These days working on web has become inevitable and thus it is very important to know the threats it offers in many ways. Safe browsing on web needs you to know many things like:
- What are the possible dangers?
- How to avoid these ?
- How to virtually conduct yourself while browsing web ?
Thus, you need to know that not every site is safe to visit; whatever you post or do online is visible to others; not everything that you see or is promised online is true. Also, safeguarding your computer is very crucial before you go online. There are some rules you must follow to conduct yourself online and there are other things that you must know so that you can counter unknown dangers.
All this and more, we are covering in coming sections.
Identity Protection While Using Internet | Web
We surf the Internet for a variety of reasons, from using social media, buying and selling goods, to sending information. When we give out private data to businesses and other Internet users (Such as while filling up some forms or making payments online), we trust them to use that information for legitimate purposes. This isn’t always the case though and financial and personal data can be used for harmful reasons like hacking, stalking and identity fraud. Identity fraud is when personal details that have been accessed or stolen are used to commit fraudulent acts posing as someone else with stolen identity.
Most common solution to this is :
Private browsing or Anonymous Browsing on Internet. Before we talk about this, let us talk about what happens when you normally browse the Internet.
Many Ways Websites Track you
Whenever you visit a website, your web browser may reveal your location via your device’s IP address. It can also provide your search and browsing history etc. which may be used by third parties, like advertisers or criminals. This way websites track you. Tracking is generally used by advertising networks to build up detailed profiles for pinpoint ad-targeting even tracking down users for special purpose such as effecting their political choices. Recall the data tracking reported in US elections, Brazil elections and many more.
The type of information is compiled through your web usage patterns, and which websites generally use for tracking you. This generally includes:
(a) IP Address
IP address is a unique address of your device when you connect to the Internet. It’s likely that your computer shares your IP address with the other networked devices in your house or office. From your IP address, a website can determine your rough geographical location.
(b) Cookies and Tracking Scripts
Cookies are small pieces of information websites can store in your browser. They have plenty of legitimate uses for example, when you sign into your online-banking website, a cookie remembers your login information. When you change a setting on a website, a cookie stores that setting so it can persist across page loads and sessions e.g., you change the zoom percentage of your webpage, then this setting will reflect on all opened webpages – because this was stored in a cookie. Cookies can also identify you and track your browsing activity across a website.
Cookies can be:
(i) First party cookies.
These are the cookies that store your own login id, passwords, auto till information etc. for some websites that you frequently visit.
(ii)Third party cookies.
These are the cookies that websites store to know about our Search history and web browsing history so as to place advertisements as per your interests.
Third party cookies may result in many unwanted advertisements on your webpages.
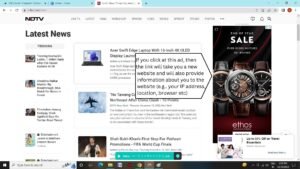
(c) HTTP Referrer
When you click a link, your browser loads the web page linked to it and tells the website where you came from. For example, if you clicked a link to an outside website on a webpage eg., (see figure below) then the linked website will get opened and internally information about you such as your IP address, location, your web browser, machine type etc. will also be provided to the linked website -it is known as the HTTP referrer (e.g., see figure below).
(d) Super Cookies
Super cookies are also cookies but these are persistent cookies, i.e., they come back even after you delete them. Super cookies (like evercookie) store cookie data in multiple places – for example, in Flash cookies, Silverlight storage, your browsing history, and HTML5 local storage etc.
When a website notices that you’ve deleted part of the super cookie, the information 1s repopulated from the other location. For example, you might clear your browser cookies and not your Flash cookies, so the website will copy the value of the Flash cookies to your browser cookies.
(e) User Agent
Your browser also sends a user agent every time you connect to a website. This tells websites your browser and operating system, providing another piece of data that can be stored and used to target ads.
All the above things leak your identity information to websites and it may be used against you Solution to this is Private browsing and Anonymous browsing. Let us learn what is this type of browsing.
Private Browsing and Anonymous Browsing
Anonymous browsers allow users to view websites without revealing any personal information of the user like their IP address, machine type, location etc. An anonymous browser lets users access websites anonymously. It can be used as a tool for governments, journalists and everyday security-conscious surfers.
There is another type of browsing – Private browsing.
Private Browsing
There are other ways to use the Internet without revealing your search history and sharing your data. These are:
- Incognito browsing opens up a version of the browser that will not track your activity. It’s particularly useful if you’re entering sensitive data like bank details into the browser, as it can minimize the risk of your information being saved to that computer. It can also be used for purposes like – to look at surprise gifts for the family without leaving clues, searching for hotel rooms for your vacation, filling examination forms etc. But this information is still visible to your school, university or organization. You may also use private browsers and search engines like DuckDuckgo.
- Proxy works by acting as a middleman between your computer and the website you want to access. Now the tracking website will get the IP address and information that belongs to the proxy site, so you are effectively getting the same content from another source without it getting to know your browsing details.
- Virtual Private Network or a VPN is a method used to add security and privacy to private and public networks, like Wi-Fi hotspots and the Internet. VPNs are most often used by corporations to protect sensitive data. Virtual Private Networks (VPN) were originally meant for business employees working offsite to gain access to
shared drives or networks. Nowadays, you can set up a VPN at home to protect yourself from hackers trying to access your sensitive information.
CONFIDENTIALITY OF INFORMATION
Internet is a public platform, mostly. The sites you visit, the things you search on it, the posts that you put on social networking sites are all visible to public. But there must be some information like your credit history or bank details, your mails etc., which you do not want to make public, i.e., you want to keep this information confidential. Similarly, On your computer system or in a private network, you would certainly crucial information is protected and is not publically visible. Confidentiality of information ensures that only authorized users get access to sensitive and protected data.
Practices to Ensure Confidentiality of Information
Computers, networking, Internet these all are inevitable ; you cannot avoid these as these are modern age tools. But you surely can follow certain practices to safeguard your data and ensure its confidentiality.
Best practices used to ensure confidentiality are as follows:
1. Use firewall wherever possible
Your system must be secured such that only authentic users can connect to it. Firewall 1s One very good solution for this. Firewall is a program that monitors all communications and trap all illicit packets. Most operating systems now come with a firewall preinstalled. However, some, such as the Windows Firewal1, only block suspect incoming communications, leaving completely open access to the Internet from your machine.
Thus, it is recommended that you install a firewall that can monitor both incoming ana outgoing communication and traps the illicit ones.
2. Control browser settings to block tracking
You already know that websites can track your surfing on their site by IP address and related system information, including system names and Internet network addresses that often uniquely 1dentity your computer. Search engines generally record your queries together with your computer identification, building up a profile of your interests over time.
To minimize these threats, you can turn your default browser settings to exclude cookies especially third party cookies, since they can be used to build up detailed profiles of your sorting patterns over time.
3. Browse privately wherever possible
To avoid the tracking by websites, you should try to browse Internet privately wherever possible. This way websites would not be able to store cookies on your computer, which give information about your search pattern and surf history.
4. Be careful while posting on Internet
You should know that posting is public. When you post anything to a public Internet such as social networking sites like Instagram or Facebook etc., newsgroup, mailing list, or chat room, you generally give up the rights to the content and any expectation ot privacy or confidentiality is useless. In most countries, anything you post to a public space can be saved, archived, duplicated, distributed, and published, even years later, by anyone in the same way as a photograph taken in a public space like a city park.
So ensure that you never post your crucial information like your personal details such as address, mobile phone number, bank details, credit card details etc. on public Internet sites.
5. Ensure Safe sites while entering crucial information
Sometimes, you have a need to provide your crucial information such as your personal details or bank details etc. For example, you might be applying online to register for an entrance exam through a legitimate site that asks for your personal details.
In such cases, ensure these things :
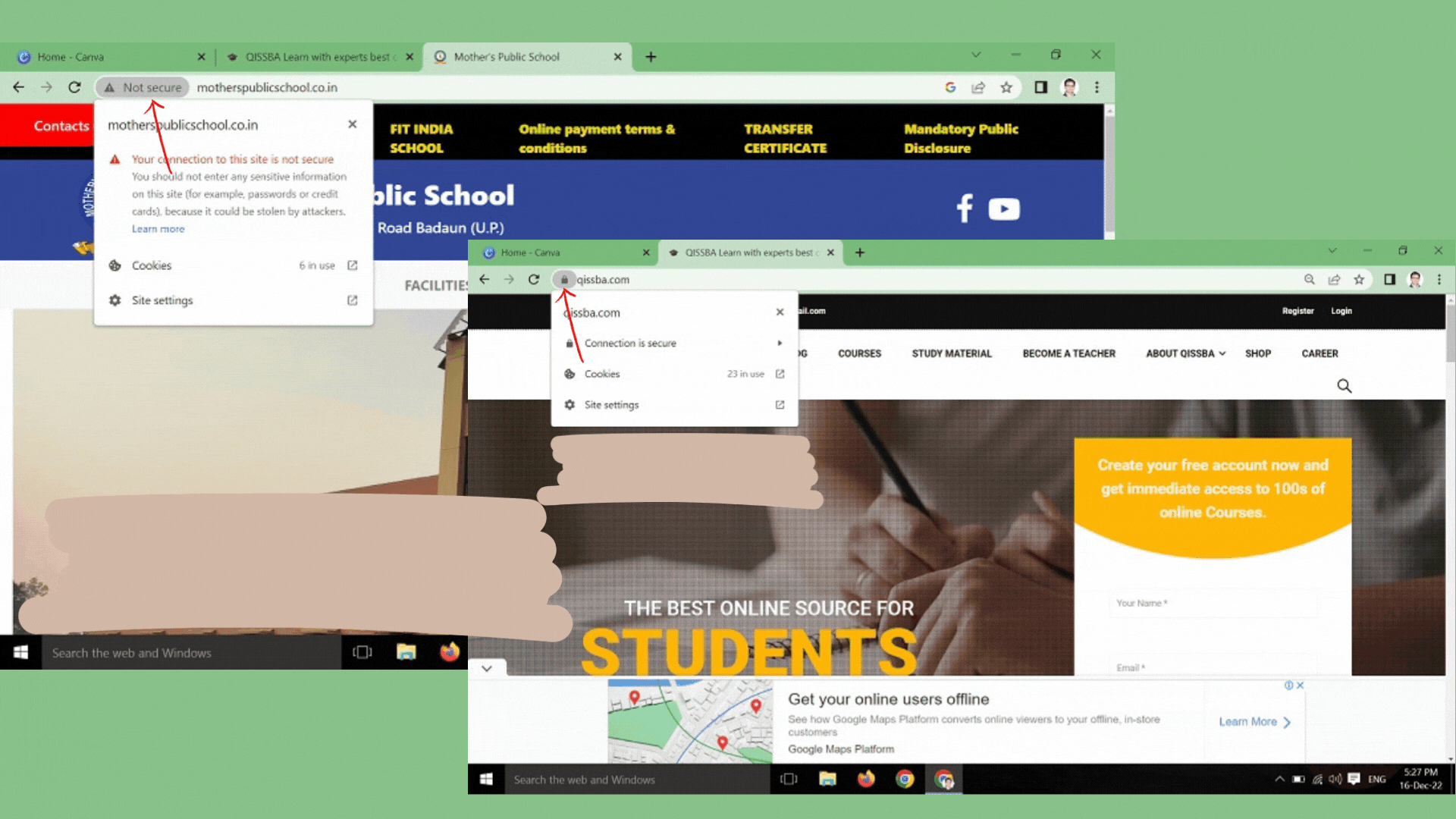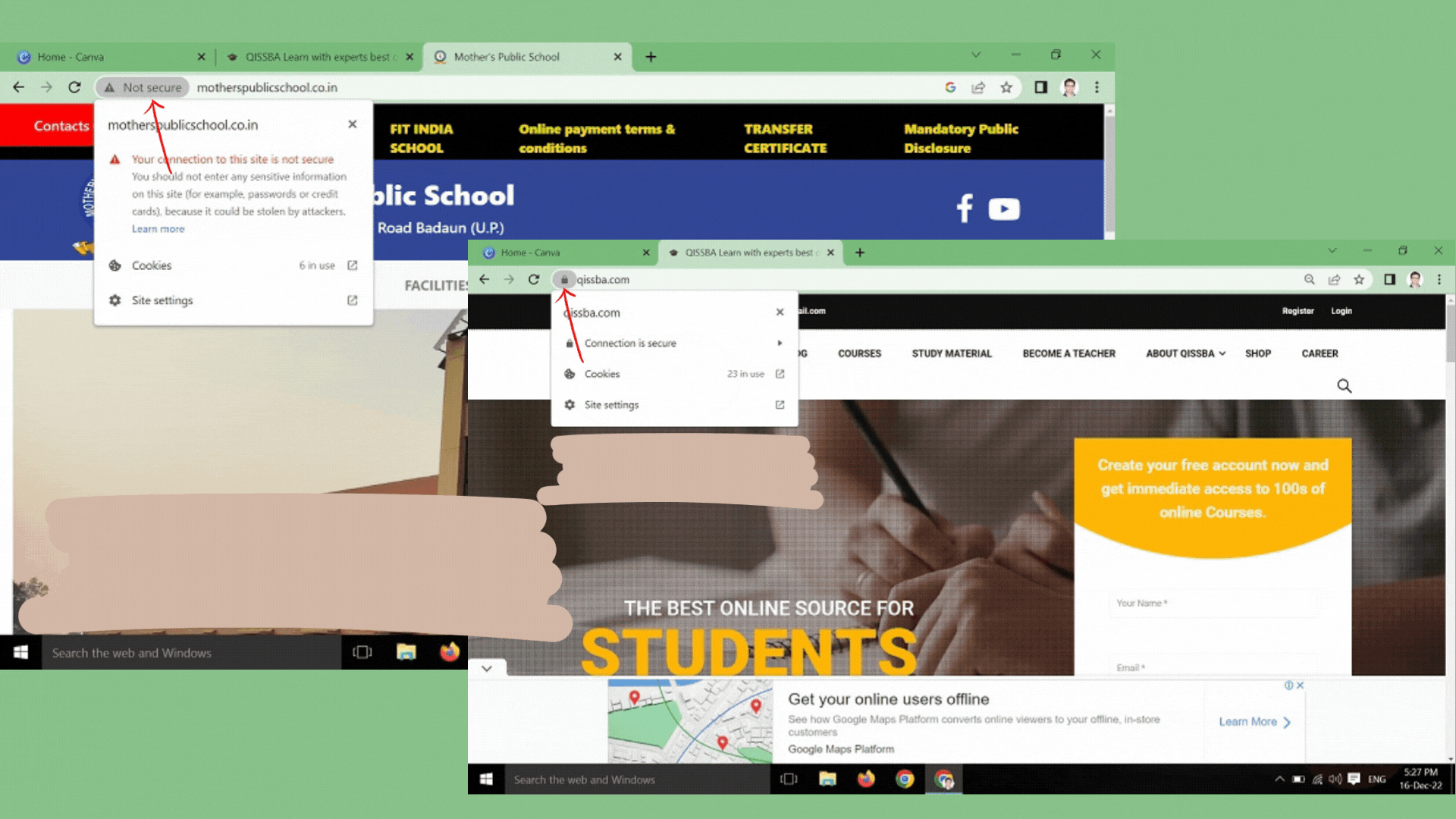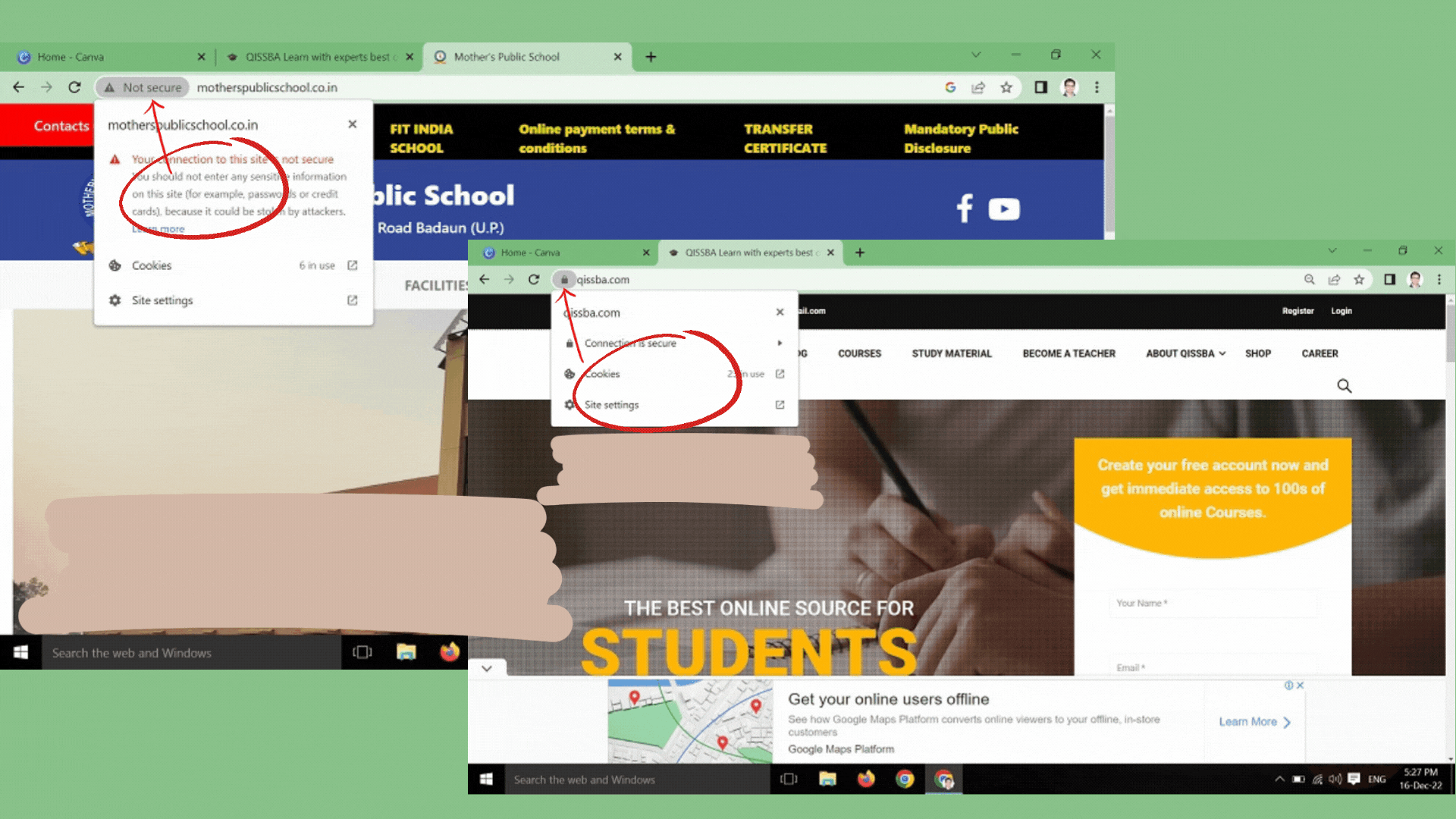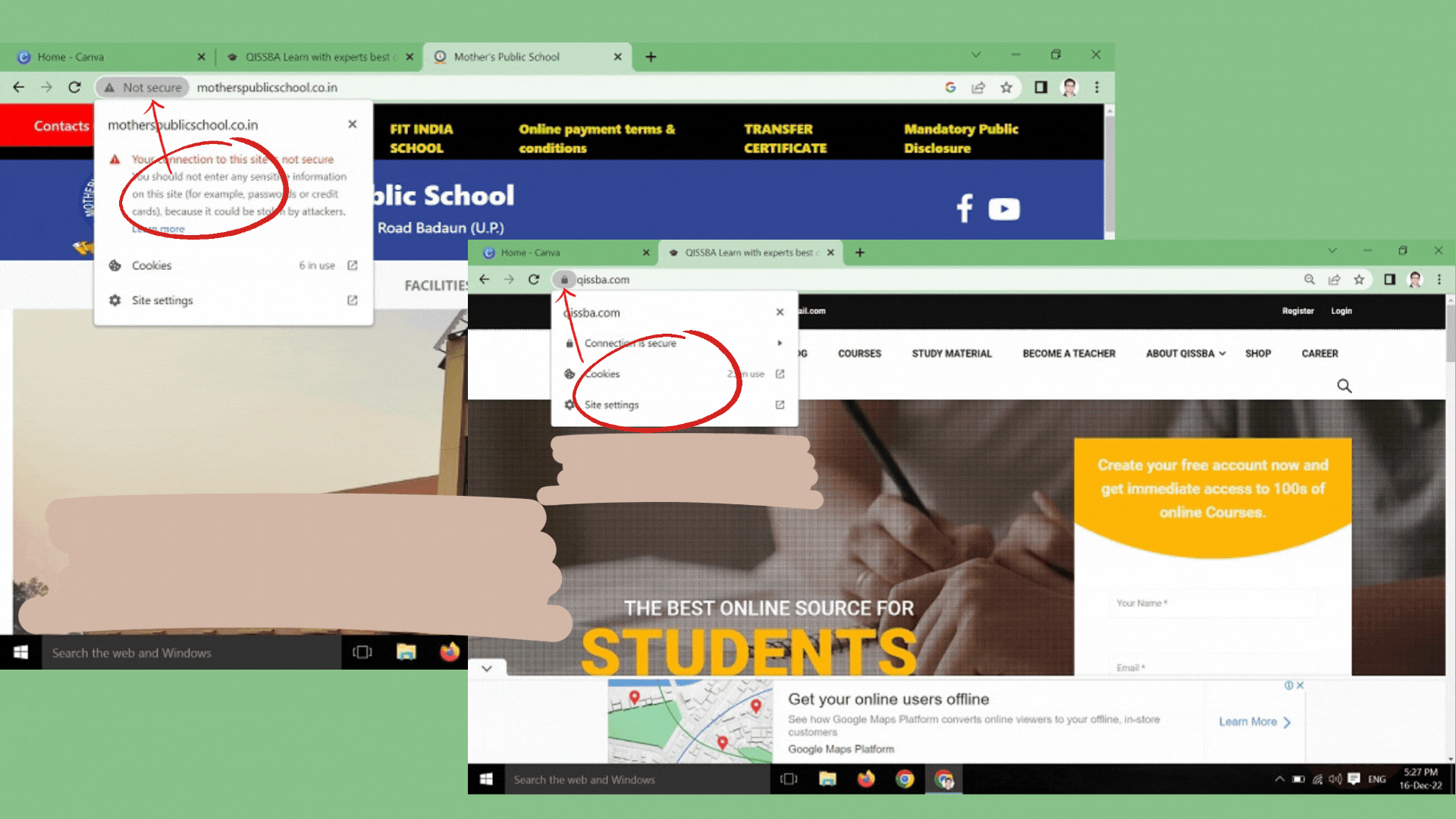
- Type the URL of the website in the address bar of the browser on your own. Do not click on a link that takes to this website; or do not cut/copy the link of this website and paste it. TYPE THE URL ON YOUR OWN in the address bar of the web browser.
- Ensure that the address contains HTTP and a pad lock sign. When this website gets loaded, before you start typing any information, ensure that the website address. A safe
site’s URL starts with https:// and not with http://. Also, it shows a closed pad lock.
6. Carefully handle emails
While opening an email, make sure that you know the sender. Even if you open the email message by accident, make sure not to open attachment in an email from unrecognized source Emails containing sensitive information should be deleted securely.
Also, your email might contain a link to legitimate looking website; never click on any link inside an email to open it. The link might look legit but it may take you to a fraudulent site. Even if you need to visit the linked website, type the URL of the website on your own in the address bar of a web browser but never open any link by clicking inside an email or by copying its link.
7. Do not give sensitive information on wireless networks
Sometimes, you get access to some wireless connections such as the Wi-Fi connections available on Airports or Railway stations. While using such Wi-Fi connections, make sure not to open any personal email or provide any sensitive information on a website. The reason for this is that most free Wireless networks are not encrypted and hence information on it can be tapped and used for fraudulent purposes.
8. Avoid using public computers
Always try not to use the public computer especially if you have to deal with your crucial data. But if you need to work on a public computer, then make sure following things
(a) Browse privately, first of all.
(b) Don’t save your login information.
(c) Never save passwords while working on a public computer.
(d) Avoid entering sensitive information onto a public computer.
(e) Don’t leave the computer unattended with sensitive information on the screen.
(f) Disable the feature that stores passwords.
(g) Properly log out before you leave the computer.
(h) Erase history and traces of your work, i.e., clear history and cookies.