Variables and Assignments in Python | CBSE Class 12
VARIABLES AND ASSIGNMENTS
Variables represent labelled storage locations, whose values can be manipulated during program run.
In python ,to create a variable, just assign to its name the value of appropriate type. For example, to create a variable namely Student to hold student’s name and variable age to hold student’s age, you just need to write somewhat similar is shown below:
Student=” Jacob”
Age=16
Python will internally create labels referring to these values as shown below.
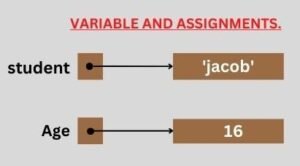
Creating a variable
Let’s take statement we used just now to create the variable marks:
Marks = 70
As you can see, that we just assigned the value of numeric type to an identifier name and python created the variable of the type similar to the type of value assigned. In short, after the above statement, we can say that marks is a numeric variable.
So, creating variable, just assign to it name the value of appropriate type. For example, to create a variable namely student to hold student ‘s name and variable age to hold student’s age, you just need to write somewhat similar to what is shown below:
Student = ‘Jacob’
Age = 16
Python will internally create labels referring to these value as shown below:
Isn’t it simple?? 😊okay, let ‘s now create some more variable.
Train No = ‘T#1234’ #variable created of string type
Balance = 23456.75 #variable created of numeric (floating point) type
roll No = 105 #variable created of numeric (integer) type
some, way you can create as many variables as you need for your program.
Multiple assignments
Python Is a very versatile with assignment. let’s see in how many different ways, you can use assignment in python.
1. Assigning some value to multiple variables
You can assign same value to multiple variables in a single statement, e.g.,
a = b = c = 10
it will assign value 10 to all three-variable a, b, c. that is all three labels a, b, c will refer to same location with value 10.
2. Assigning multiple value to multiple variables
You can even assign multiple values to multiple variables in singles statement, e.g.,
x, y, z = 10,20,30
it will assign the value order wise, i.e., first variable is given first value, second variable the second value and so on. That means, above statement will assign value 10 to x,20 to y and 30 to z.
this style of assigning value is very useful is very useful and compact. for example, consider the code given below:
X, y, = 25,50
print (X, y)
it will print result as
25 50
Because x is having value 25 and y is having 50. Now, if you want to swap value of x and y you just need to write:
X, y = y, x
Print (x, y)
Now the result will be
50 25
Because this time the value has been swapped and x is having value 25 and y is having 50. while assigning value through multiple assignments, please remember that python first evaluates the RHS (right hand side) expression (s) and then to LHS (left hand side), e.g.,
A, b, c = 5,10,7 #stament1
B, c, a=a + 1, b + c, c-1 #statement2
Print (a, b, c)
- Statement 1assign 5,10 and 7 to a, band c respectively.
- Statement2 will first evaluate RHS i.e., a +1, b + 2, c – 1 which will yield
5 + 1, 10 +2, 7 – 1 = 6, 12, 6
Then it will make the statement (by replacing the evaluated result of RHS) as :
b, c, a = 6, 12, 6
Thus, b = 6, c=12 and a = 6
- The third statement print (a, b, c) will print
6 6 12
Isn’t this easy? now can you guess the output of following code fragment2
P, q = 3
q, r = p – 2, p+2
print (p, q, r)
please note the expression separated with commas are evaluated from left to right and assigned in same order e.g.,
x = 10
y, y = x + 2, x + 5
will evaluate to following (after evaluating expression on RHS = Operator)
y, y = 12,15
i.e., firstly, it will assign first RHS value to first LHS variable i.e.,
y = 12
then it will assign second RHS value to second LHS variable i.e.,
y = 5
so, if you print y after this statement y will contain 15.
Now, consider following code and guess the output:
x, x = 20, 30
y, y = x + 10, x + 20
Print (x, y)
Well, it will print the output as
30 50
Now you know why? 😊


