
Python Full Course for Beginners | Complete All-in-One Guide | CBSE Class 11
Introduction to Our Python Course for Beginners
How to Learn Python Programming from Scratch in 2025 | An Expert Method Guide
Hello student !!! welcome you all, in this tutorial, we are going to discuss the syllabus of Python Full Course for beginners with CBSE Class 11 that is, whatever is your syllabus in 2025 and 2026, we will discuss what will be your board exam in 2025, so what is the syllabus for the exam 2026 and how you have to prepare, we will discuss all those things in this tutorial, so read this tutorial carefully so that all your doubts are cleared and get to know how you have to prepare. For board exam and I will tell you complete details how you will prepare.
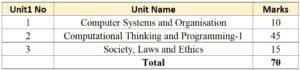
This tutorial in your hands is based on revised syllabus by CBSE for ‘Computer Science’ code 083, class XI. This syllabus has been divided into three units:
Unit 1: Computer Systems and Organisation (CSO)
Computer Systems and Organisation unit has been divided in four chapters, Chapters 1 to 4. This unit coves basic computer organisation, Boolean logic, data representation and insight into program execution. The aim of this unit is to give an idea of how the information is represented, organized and processed inside a computer.
Unit 2: Programming and Computational Thinking (PCT-1)
Programming and Computational Thinking unit has been divided in 10 chapters, Chapters 5 to 14. This unit covers basics of Python, fundamentals, conditional and iterative constructs, strings, lists, tuples, dictionaries, sorting and program debugging techniques. The aim of this unit is to lay foundation of problem-solving skills through Python programming language.
Unit 3: Society, Law and Ethics (SLE-1)
Society, Law and Ethics unit has been divided into two chapters, Chapters 19 to 20. This unit covers Cyber safety basics and guidelines, guidelines and usage rules for using social networks, threats while accessing websites and how to prevent/counter these along with how to securely communicate data. The aim of this unit is to know the challenges in safe and secure use of cyber facilities and technologies to counter these.
==============================================================================
Apart from this blog tutorial, we have also provided a Python Full Course for Beginners in our courses section that contains additional practice exercises. Although this tutorial contains sufficient number of practice questions and exercises, yet the additional practice of exercises given in our Python full courses for beginners that will make the foundation of programming and other concepts even stronger.

Python Full Course for Beginners from Scratch
Computer Science is a rapidly evolving field. In fact, to keep pace with its developments, every field related to Computer Science has to evolve to match the steps. ‘Education’ field is no exception. After introduction of new syllabus for the subject ‘Computer Science’ (code 083) this year 2025-26, CBSE has again introduced something more interesting in the syllabus for the same for CBSE class XI.
Now let’s have a deep dive into the detailed topic wise Syllabus with links to Python Full Course for Beginners for CBSE Class 11th students.

Unit 1: Computer Systems and Organisation (CSO)
● Basic computer organisation: Introduction to Computer System, hardware, software, input device, output device, CPU, memory (primary, cache and secondary), units of memory (bit, byte, KB, MB, GB, TB, PB)
● Types of software: System software (Operating systems, system utilities, device drivers), programming tools and language translators (assembler, compiler, and interpreter), application software
● Operating System(OS): functions of the operating system, OS user interface ● Boolean logic: NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR, XOR, truth tables and De Morgan’s laws, Logic circuits
● Number System: Binary, Octal, Decimal and Hexadecimal number system; conversion between number systems
● Encoding Schemes: ASCII, ISCII, and Unicode (UTF8, UTF32)
Unit 2 : Programming and Computational Thinking (PCT-1)
● Introduction to Problem-solving: Steps for Problem-solving (Analyzing the problem, developing an algorithm, coding, testing, and debugging), representation of algorithms using flowchart and pseudocode, decomposition
● Familiarization with the basics of Python programming: Introduction to Python, Features of Python, executing a simple “hello world” program, execution modes: interactive mode and script mode, Python character set, Python tokens( keyword, identifier, literal, operator, punctuator), variables, concept of l-value and r-value, use of comments
● Knowledge of data types: Number(integer, floating point,complex), boolean, sequence(string, list, tuple), None, Mapping(dictionary), mutable and immutable data types.
● Operators: arithmetic operators, relational operators, logical operators, assignment operators, augmented assignment operators, identity operators (is, is not), membership operators (in not in)
● Expressions, statement, type conversion, and input/output: precedence of operators, expression, evaluation of an expression, type-conversion (explicit and implicit conversion), accepting data as input from the console and displaying output.
● Errors- syntax errors, logical errors, and run-time errors
● Flow of Control: introduction, use of indentation, sequential flow, conditional and iterative flow
● Conditional statements: if, if-else, if-elif-else, flowcharts, simple programs: e.g.: absolute value, sort 3 numbers and divisibility of a number.
● Iterative Statement: for loop, range(), while loop, flowcharts, break and continue statements, nested loops, suggested programs: generating pattern, summation of series, finding the factorial of a positive number, etc.
● Strings: introduction, string operations (concatenation, repetition, membership and slicing), traversing a string using loops, built-in functions/methods–len(), capitalize(), title(), lower(), upper(), count(), find(), index(), endswith(), startswith(), isalnum(), isalpha(), isdigit(), islower(), isupper(), isspace(),lstrip(), rstrip(), strip(), replace(), join(), partition(), split()
● Lists: introduction, indexing, list operations (concatenation, repetition, membership and slicing), traversing a list using loops, built-in functions/methods–len(), list(), append(), extend(), insert(), count(), index(), remove(), pop(), reverse(), sort(), sorted(), min(), max(), sum(); nested lists, suggested programs: finding the maximum, minimum, mean of numeric values stored in a list; linear search on list of numbers and counting the frequency of elements in a list.
● Tuples: introduction, indexing, tuple operations (concatenation, repetition, membership and slicing); built-in functions/methods – len(), tuple(), count(), index(), sorted(), min(), max(), sum(); tuple assignment, nested tuple; suggested programs: finding the minimum, maximum, mean of values stored in a tuple; linear search on a tuple of numbers, counting the frequency of elements in a tuple.
● Dictionary: introduction, accessing items in a dictionary using keys, mutability of a dictionary (adding a new term, modifying an existing item), traversing a dictionary, built-in functions/methods – len(), dict(), keys(), values(), items(), get(), update(), del, clear(), fromkeys(), copy(), pop(), popitem(), setdefault(), max(), min(), sorted(); Suggested programs: count the number of times a character appears in a given string using a dictionary, create a dictionary with names of employees, their salary and access them.
● Introduction to Python modules: Importing module using ‘import ’ and using from statement, importing math module (pi, e, sqrt(), ceil(), floor(), pow(), fabs(), sin(), cos(), tan()); random module (random(), randint(), randrange()), statistics module (mean(), median(), mode()).
Unit 3: Society, Law and Ethics (SLE-1)- Cyber safety
● Digital Footprints
● Digital Society and Netizen: net etiquettes, communication etiquettes, social media etiquettes
● Data Protection: Intellectual property rights (copyright, patent, trademark), violation of IPR (plagiarism, copyright infringement, trademark infringement), open source software and licensing (Creative Commons, GPL and Apache)
● Cyber Crime: definition, hacking, eavesdropping, phishing and fraud emails, ransomware, cyber trolls, cyber bullying
● Cyber safety: safely browsing the web, identity protection, confidentiality
● Malware: viruses, trojans, adware
● E-waste management: proper disposal of used electronic gadgets.
● Information Technology Act (IT Act)
● Technology and society: Gender and disability issues while teaching and using computers
PRACTICAL

Programming in Python
At least the following Python concepts should be covered in the lab sessions: expressions, conditionals, loops, list, dictionary, and strings. The following are some representative lab assignments.
- Find the largest and smallest numbers in a list.
- Test for primarily.
- Find the third largest number in a list.
- Find whether a string is a palindrome or not.
- Given two integers x and n, computer x”.
- Compute the greatest common divisor and the least common multiple of two integers.
- Test if a number is equal to the sum of the cubes of its digits. Find the smallest and largest such numbers.
Syllabus Content Python Full Course for Beginners
1 COMPUTER SYSTEM OVERVIEW
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Basic Computer Organization
- Input Unit
- Output Unit
- The CPU (Central Processing Unit)
- The Memory [Main Memory/Primary Memory]
- The Storage Unit
- The System Bus
1:3 Mobile System Organization
1.4 Types of Software
- System Software
- Application Software
- Software Libraries
2 DATA REPRESENTATION
2.1 Introduction
2.2 Digital Number Systems
- Decimal Number System
- Binary Number System
- Octal Number System
- Hexadecimal Number System
2.3 Number Conversions
- Decimal-to-Binary Conversion
- Binary-to-Decimal Conversion
- Decimal-to-Octal Conversion
- Octal-to-Decimal Conversion
- Octal-to-Binary Conversion
- Binary-to-Octal Conversion
- Decimal-to-Hex Conversion
- Hex-to-Decimal Conversion
- Binary-to-Hex Conversion
- Hex-to-Binary Conversion
2.4 Representing Unsigned Integers in Binary
2.5 Binary Addition
2.6 Character/String Representation
- ASCII Code
- ISCII Code
- Unicode
3 BOOLEAN LOGIC
3.1 Development of Boolean Logic
3.2 Binary Valued Quantities
3.3 Logical Operations
- Logical Function or Compound Statement
- Logical Operators
- Evaluation of Boolean Expressions using Truth Table
3.4 Basic Logic Gates
- Inverter (NOT Gate)
- OR Gate
- AND gate
3.5 Basic Postulates of Boolean Logic
3.6 Principle of Duality
3.7 Basic Theorems of Boolean Algebra/Logic
- Properties of 0 and 1
- Idempotence Law
- Involution
- Complementarity Law
- Commutative Law
- Associative Law
- Distributive Law
- Absorption Law
- Some Other Rules of Boolean Logic Algebra
3.8 DeMorgan’s Theorems
- DeMorgan’s First Theorem
- DeMorgan’s Second Theorem
3.9 More about Logic Gates
- NOR Gate
- NAND Gate
- XOR Gate (Exclusive OR Gate)
- XNOR Gate (Exclusive NOR gate)
4 INSIGHTS INTO PROGRAM EXECUTION
4.1 Introduction
4.2 Basic Flow of Compilation
4.3 Understanding Translation Process
- The Compilation Process
- The Interpretation Process
4.4 Role of an Operating System in Running a Program
4.5 Introduction to Parallel Computing
4.6 Cloud Computing
5 COMPUTATIONAL THINKING AND GETTING STARTED WITH PYTHON
5.1 Introduction
5.2 Computational Thinking
5.3 Python-Pluses
5.4 Python-Some Minuses (So Human Like)
5.5 Working in Python
- Working in Default CPython Distribution
- Working in Anaconda Distribution
- Writing and Compiling Python Program with Command Line in Linux
5.6 Understanding First Program/Script
6 PYTHON FUNDAMENTALS
6.1 Introduction
6.2 Python Character Set
6.3 Tokens
6.4 Barebones of a Python Program
6.5 Variables and Assignments
- Creating a Variable
- Multiple Assignments
- Variable Definition
- Dynamic Typing
6.6 Simple Input and Output
- Reading Numbers
- Output Through print() Statement
7 DATA HANDLING
7.1 Introduction
7.2 Data Types
- Numbers
- Strings
- Lists and Tuples
- Dictionary
7.3 Mutable and Immutable Types
- Variable Internals
7.4 Operators
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Identity Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Operator Precedence
7.5 Expressions
- Evaluating Expressions
- Type Casting
7.6 Working with Some Standard Library Modulus
- Working with math Module of Python
- Using random Module
- Using the statistics Module
8 CONDITIONAL AND ITERATIVE STATEMENTS
8.1 Introduction
8.2 Types of Statements in Python
8.3 Statement Flow Control
8.4 Program Logic Development Tools
- Flowcharts
- The if Statements of Python
- The if Statement
- The if-else Statement
- The if-elif Statement
- The nested if Statement
8.6 Repetition of Tasks – A Necessity
8.7 The range() Function
8.8 Iteration/Looping Statements
- The for Loop
- The while Loop
- Loop else Statement
- Jump Statements – break and continue
- Loop else Statement
- Nested Loops
9 STRING MANIPULATION
9.1 Introduction
9.2 Traversing a String
9.3 String Operators
- Basic Operators
- Membership Operators
- Comparison Operators
9.4 String Slices
9.5 String Functions and Methods
10 DEBUGGING PROGRAMS
10.1 Introduction
10.2 What is Debugging?
10.3 Errors and Exceptions
- Errors in a Program
- Exceptions
10.4 How to Debug a program?
- Debugging Techniques
10.5 Using Debugger Tool
- Working with Integrated Debugger Tool of Spyder IDE
- Working with Python Debugger-pdb
11 LIST MANIPULATION
11.1 Introduction
11.2 Creating and Accessing Lists
- Creating Lists
- Accessing Lists
11.3 List Operations
- Joining Lists
- Repeating or Replicating Lists
- Slicing the Lists
11.4 Working with Lists
11.5 List Functions and Methods
12 TUPLES
12.1 Introduction
12.2 Creating and Accessing Tuples
- Creating Tuples
- Accessing Tuples
12.3 Tuple Operations
- Joining Tuples
- Slicing the Tuples
12.4 Tuple Functions and Methods
13 DICTIONARIES
13.1 Introduction
13.2 Dictionary – Key: Value Pairs
13.2.1 Creating a Dictionary
13.2.2 Accessing Elements of a Dictionary
13.2.3 Characteristics of a Dictionary
13.3 Working with Dictionaries
13.3.1 Multiple Ways of Creating Dictionaries
13.3.2 Adding Elements to Dictionary
13.3.3 Updating Existing Elements in a Dictionary
13.3.4 Deleting Elements from a Dictionary
13.3.5 Checking for Existence of a Key
13.3.6 Pretty Printing a Dictionary
13.3.7 Counting Frequency of Elements in a List using Dictionary
13.4 Dictionary Functions and Methods
14 UNDERSTANDING SORTING
14.1 Introduction
14.2 What is Sorting?
14.3 Bubble Sort
14.4 Insertion Sort
15 RELATIONAL DATABASES
15.1 Introduction
15.2 Purpose of DBMS
15.3 Relational Database Model
15.4 The Relational Model Terminology
15.4.1 Views
15.4.2 Structure of Relational Databases
15.5 Brief History of MySQL
15.6 MySQL Database System
15.7 Starting MySQL
15.8 MySQL and SQL
15.8.1 Processing Capabilities of SQL
15.8.2 Data Definition Language
15.8.3 Classification of SQL Statements
16 SIMPLE QUERIES IN SQL
16.1 Introduction
16.2 Some MySQL SQL Elements
16.2.1 Literals
16.2.2 Data Types
16.2.3 Null Values
16.2.4 Comments
16.3 SQL Command Syntax
16.4 Sample Database
16.5 Making Simple Queries
16.5.1 Accessing Database
16.5.2 The SELECT Command
16.5.3 Selecting All Columns
16.5.4 Reordering Columns in Query Results
16.5.5 Eliminating Redundant Data (with keyword DISTINCT)
16.5.6 Selecting from all the Rows – ALL Keyword
16.5.7 Viewing Structure of Table
16.5.8 How to Perform Simple Calculations?
16.5.9 Scalar Expressions with Selected Fields
16.5.10 Using Column Aliases
16.5.11 Handling Nulls
16.5.12 Putting Text in the Query Output
16.5.13 Selecting Specific Rows – WHERE clause
16.5.14 Relational Operators
16.5.15 Logical Operators
16.5.16 Condition Based on a Range
16.5.17 Condition Based on a List
16.5.18 Condition Based on Pattern Matches
16.5.19 Searching for NULL
16.5.20 Operator Precedence
16.5.21 Sorting Results – ORDER BY clause
16.6 MySQL Functions
16.6.1 String Functions
16.6.2 Numeric Functions
16.6.3 Date and Time Functions
16.7 Aggregate Functions
17 PABLE CREATION AND DATA MANIPULATION COMMANDS
17.1 Introduction
17.2 Databases in MySQL
17.2.1 Creating Databases
17.2.2 Opening Databases
17.2.3 Removing Databases
17.3 Creating Tables
17.3.1 Data Integrity Through Constraints
17.4 Changing Data with DML Commands
17.4.1 Inserting Data into Table
17.4.2 Modifying Data with UPDATE Command
17.4.3 Deleting Data with DELETE Command
17.5 More DDL Commands
17.5.1 ALTER TABLE Command
17.5.2 The DROP TABLE Command
19 BASICS OF NOSQL DATABASE – MONGODB
18.1 Introduction
18.2 What are NoSQL databases?
18.2.1 Types of NoSQL Databases
18.2.2 Advantages and Disadvantages of NoSQL Databases
18.3 Working with MongoDB
18.3.1 MongoDB Terminology
18.3.2 Starting MongoDB Service
19 CYBER SAFETY
19.1 Introduction
19.2 What is Cyber Safety?
19.3 Safely Browsing The Web
19.4 Identity Protection While Using Internet
19.4.1 Many Ways Websites Track you
19.4.2 Private Browsing and Anonymous Browsing
19.5 Confidentiality of Information
19.5.1 Practices to Ensure Confidentiality of Information
19.6 Cybercrime
19.6.1 Reporting Cybercrime
19.7 Common Social Networking Sites
19.8 Appropriate Usage of Social Networks
19.8.1 What You Should Know?
19.8.2 What You should do – Usage Rules
20 ONLINE ACCESS AND COMPUTER SECURITY
20.1 Introduction
20.2 Threats to Computer Security
20.2.1 Computer Viruses
20.2.2 Spyware
20.2.3 Adware
20.2.4 Spamming
20.2.5 PC Intrusion
20.2.6 Eavesdropping
20.2.7 Phishing and Pharming
20.2.8 Cookies
20.3 Solutions to Computer Security Threats
20.3.1 Solutions to Viruses, Adware and Spyware
20.3.2 Solutions to Spam, Eavesdropping
20.3.3 Solutions to PC Intrusion
20.3.4 Solutions to Phishing and Pharming Attack
20.4 Firewall-An Important Solution for Computer Security


