Online Access and Computer Security | Virus Security – Threats and Solutions!
ONLINE ACCESS AND COMPUTER SECURITY
Introduction This tutorial talks about the threats that are associated with online access and the measures to prevent and counter them, if ever they occur. We have covered all necesory concepts required by CBSE sylaabus Class 11th.
We live in a world at a time which is often called information age where information is freely available from any part of the world. The Internet has revolutionized the world and people are getting used to having access to whatever information they want anytime, anywhere and from a wider and wider range of computing devices.
Unfortunately, this also has resulted in increased security concerns. Now, even if you ensure not to use any external media on your computers but if you are connected to the Internet, your Computer and data on it is still vulnerable.
THREATS TO COMPUTER SECURITY
A threat is a potential violation of security. When a threat is actually executed, it becomes attack. Those who execute such actions, or cause them to be executed are called attackers.
Some common threats the average computer user faces every day.
- Viruses : Worms , Trojans
- Spyware
- Adware
- Spamming
- PC Intrusion : Denial of services , Sweeping, Password Guessing
- Phishing
Computer Viruses
Computer viruses are malicious codes/programs that cause damage to data and files on a system. Viruses can attack any part of a computer’s software such as boot block, system, system areas, files and application-program-macros etc.
Two other similar programs also cause virus like effects. These are:
(a) Worms.
A worm is a self-replicating program which eats up the entire disk space or memory. A worm keeps on creating its copies until all the disk space or memory is filled.
(b) Trojan Horses.
A Trojan horse is a program that appears harmless (such as a text editor or a utility program) but actually performs malicious functions such as deleting or damaging files.
DAMAGE CAUSED BY VIRUSES
Viruses can do the following if left unchecked:
- Damage or delete files.Some viruses may delete or damage random documents or specific files that are crucial to your operating system-for example, operating system files. This damage can range from rendering useless just a few files to affecting your entire computer, possibly requiring you to reinstall your operating system and start from scratch.
- Slow down your computer.Viruses can run in the background, without being seen, and may cause your computer to run extremely slow.
- Invade your email program.Some forms of viruses may wreak even more havoc by spreading themselves to the contacts in your address book.
Spyware
Spyware is a software which is installed on your computer to spy on your activities and report this data to people willing to pay for it. It tracks the user’s behavior and reports information back to a central source. These are used to spy on some one either for legal or illegal purpose.
Spyware mostly get installed on your PC without your consent. Typically, spyware finds its way onto PCs “piggybacking” onto a file, or gets downloaded from the Internet when you visit a particular website. Fests such as spyware can often lurk silently on your computer until someone O something sets them off, or until they are found and properly removed.
DAMAGE CAUSED BY SPYWARE
Spyware can act like a peeping tom or, at worse, a geeky thief. For example, it
- Compromises your data, computing habits, and identity.Spyware can monitor information about your computing habits, such as what websites you visit, or record your keystrokes, which in the end can lead to identity theft. For example, spyware can record the keystrokes that you use while keying in a credit card number and send this number to a “cyber thief.”
- Alters PC settings.Some forms of spyware can also alter computer settings like your web browser home page setting or the placement of your desktop icons. This doesn’t do much damage to your PC, but it’s really annoying.
- Slows down your PC.Spyware can rob your PC or system speed and Internet access efficiency. This can become a big problem when you’re trying to use the programs on your PC, watch videos online, or download large files.
Adware
These are the programs that deliver unwanted ads to your computer (generally in Pop-Ups form). 1hey consume your network bandwidth. Adware is similar to spyware-however, It may be installed with your consent. So it is advised that you thoroughly read installation agreements before you allow installation of a software.
DAMAGE CAUSED BY ADWARE
Adware comes complete with the following disadvantages:
- Adware tracks information just like spyware.Adware tracks information about your data and computing habits to produce targeted advertising, such as pop-up ads, on your computer screen.
- Displays arrays of annoying advertising.When infected with adware, you will likely see frequent pop-up ads appear out of nowhere. This may even happen every time you open your web browser.
- Slows down your PC. The adware software working in the background and the bombardment of ads can slow your PC to a crawl.
Spamming
Spamming refers to the sending of bulk-mail by an identified or unidentified source. In non-malicious form, bulk- advertising mail is sent to many accounts. In malicious form (eg., e-mail bombing), the attacker keeps on sending bulk mail until the mail-server runs out of disk space.
DAMAGE CAUSED BY SPAMMING
Spamming comes complete with the following disadvantages:
- Spam reduces productivity.The billions of spam messages circulating across the Internet can disrupt email delivery, degrade system performance, and reduce overall productivity.
- Spam eats up your time.Deleting spam emails seems like the simple solution, but it eats up a significant amount of productivity.
- Spam can lead to worse things.spam messages may contain offensive or fraudulent material and can even be used to Spread viruses.
PC Intrusion
Every PC (personal computer) connected to the Internet is a potential target for hackers. Computers are under constant attack cyber vandals. PC Intrusion can occur in any of the following form.
(i) Sweeper Attack. This is another malicious program used by hackers. It sweeps i.e., deletes all the data from the system.
(ii) Denial of Services. This type or attack eats up all the resources of a system and the system or applications come to a halt. Example of such an attack is flooding a system with junk mail.
(iii) Password Guessing. Most hackers crack or guess passwords of system accounts and gain entry into remote computer systems. And then they use it for causing damages in one or another form.
Eavesdropping
Eavesdropping is a passive attack in which an attacker gains access to the communication-medium through which some communication is taking place and then listens to the communication and gets information about the content of the message.
Eavesdropping can be carried out through all communication devices and media of today- telephone systems, emails, instant messaging, other Internet services (e.g., chat rooms, social networking websites etc.), mobile devices etc. Eavesdropping activities do not affect normal operation of transmission and communication; thus both the sender and the recipient can hardly notice that the data has been stolen, intercepted or defaced.
For example, while sending emails, if the email message is not encrypted and digital signature has not been used, then the attacker can exploit these security loopholes. Because of these security lapses, the attacker can launch a Man-in-the-Middle attack on the network and intercept the message being transmitted. The attacker can then deface the message and send it to the recipient. The recipient is then deceived into believing the defaced message is the real message and may act as per the defaced message and may provide personal or sensitive information.
Similarly sending or providing confidential information over insecure protocols like HTTP makes the information more prone to eavesdropping attack.
Phishing and Pharming
It is the criminally fraudulent process of attempting to acquire sensitive information such as
usernames, passwords, credit card information account data etc. In Phishing, an imposter Uses an authentic looking email or web-site to +rick recipients into giving out sensitive personal information. For instance, you may receive . mail from your bank (which appears genuine to you) asking to update your information online by clicking at a specified link. Though it appears genuine, you may be taken to a fraudulent site where all your sensitive information is obtained and later used for cyber-crimes and frauds.
Pharming (pronounced “farming”) is an attack in which a hacker attempts to redirect a website’s traffic to another, bogus website. Through pharming attack, the attacker points you to a malicious and illegitimate website by redirecting the legitimate URL. Even if the URL is entered correctly, it can still be redirected to a fake website.
In this the attacker convinces you that the site is real and legitimate by spoofing or looking almost identical to the actual site down to the smallest details. You may enter your personal information and unknowingly give it to someone with malicious intent.
Cookies
A cookie, also known as a web cookie or a browser cookie, is a small piece of data sent from a website and stored in a user s web browser (in a text file) while a user is browsing a website. Some cookies disappear after user closes his browser while others, known as tracking cookies, remain saved and load the next time user visits the same websites.
These cookies help track user’s browsing sessions and load information faster, but create some security and privacy concerns as well. These security and privacy concerns are
1. Session Data.
When you visit a website on a regular basis, such as your email or online bank, you may not have to enter your username and password to get in. That’s because the information is being pulled from a tracking cookie. While these cookies encrypt the information they store, if somebody found out the encryption key and acquired your cookies, he could discover your passwords. While the odds of this happening are extremely small, the risk does exist.
2. Tracking Information.
When you visit certain websites with advertisements, those ads create cookies that store and track your online patterns. You may have noticed that if you go to a clothing store’s website, for example, you’ll see ads for that store when you click away to other websites. That’s because tracking cookies have relayed this information back to the advertisers, who use it to target their ads. Sometimes, your information may be sold to other companies. Some people view this as an invasion of privacy.
3. Public Computers.
While the same general threats exist for traffic cookies saved on public or shared computers as those saved on your personal computer, the much larger amount of people who have access to these computers makes saving traffic cookies more risky. When you finish using a public or shared computer, delete the cookies to ensure that the next people who use the same computer can’t access the information.
Solutions to Computer Security Threats
The entire computer security is based on a system of actions and safeguards that are designed to protect a computer system from deliberate (or accidental) access and/or damage by these threats. In this section, we are going to categorize the solutions to these threats in two ways
- Active protection
- Preventive measures
Active Protection
Installing and properly using an antivirus software that includes internet security – which includes protection against threats such as viruses, spyware, and PC intrusion- is vital for proper protection against the hackers, intruders, and other wrongdoers.
Preventive Measures
Even though security programs may actively detect and eliminate any threats your PC encounters, you should always help to prevent these issues from ever arising.
Let us now move on to the real solutions to the threats that we have discussed so far.
Solutions to Viruses, Adware and Spyware
There are thousands of viruses, Spyware and other Malware currently “in the wild,” and more appear each week, so protecting your systems against infection by viruses is an essential n information security. Protecting yourself against viruses involves the following safeguards:
Active Protection
- Use Anti-Virus and Anti-Spyware software.
You need these programs help to detect and eliminate any malware that sneaks its way onto your PC. If a virus somehow is found on a system on your network, you should do the following:- Scan all your systems for evidence of the virus.
- Disconnect any infected systems immediately from your network.
- Restore the infected systems from a clean backup.
- Notify your antivirus vendor so it can ensure its signature database is up-to-date.
- Download updates regularly.
New viruses and other malware emerge everyday, and your security software needs to know about them in order to provide full protection. This is done through signature file updates, so that your anti virus is laden with all new emerging viruses.
To keep you antivirus, anti-spyware program updated, the best option is to set the program to automatically updatewhen needed, so you don’t have to worry-you’ll always be fully protected. - Run frequent full-system scans.
Even though most security software programs actively scan your PC for malware, you should also pertorm a full system scan at least once a month.
Preventive Measures
- Keep your system up-to0-date.
Malware often takes advantage of security holes in operating systems and software programs. You should always install any available updates for your operating system, such as Windows, and any common software you use. - Use caution when downloading files on the Internet.
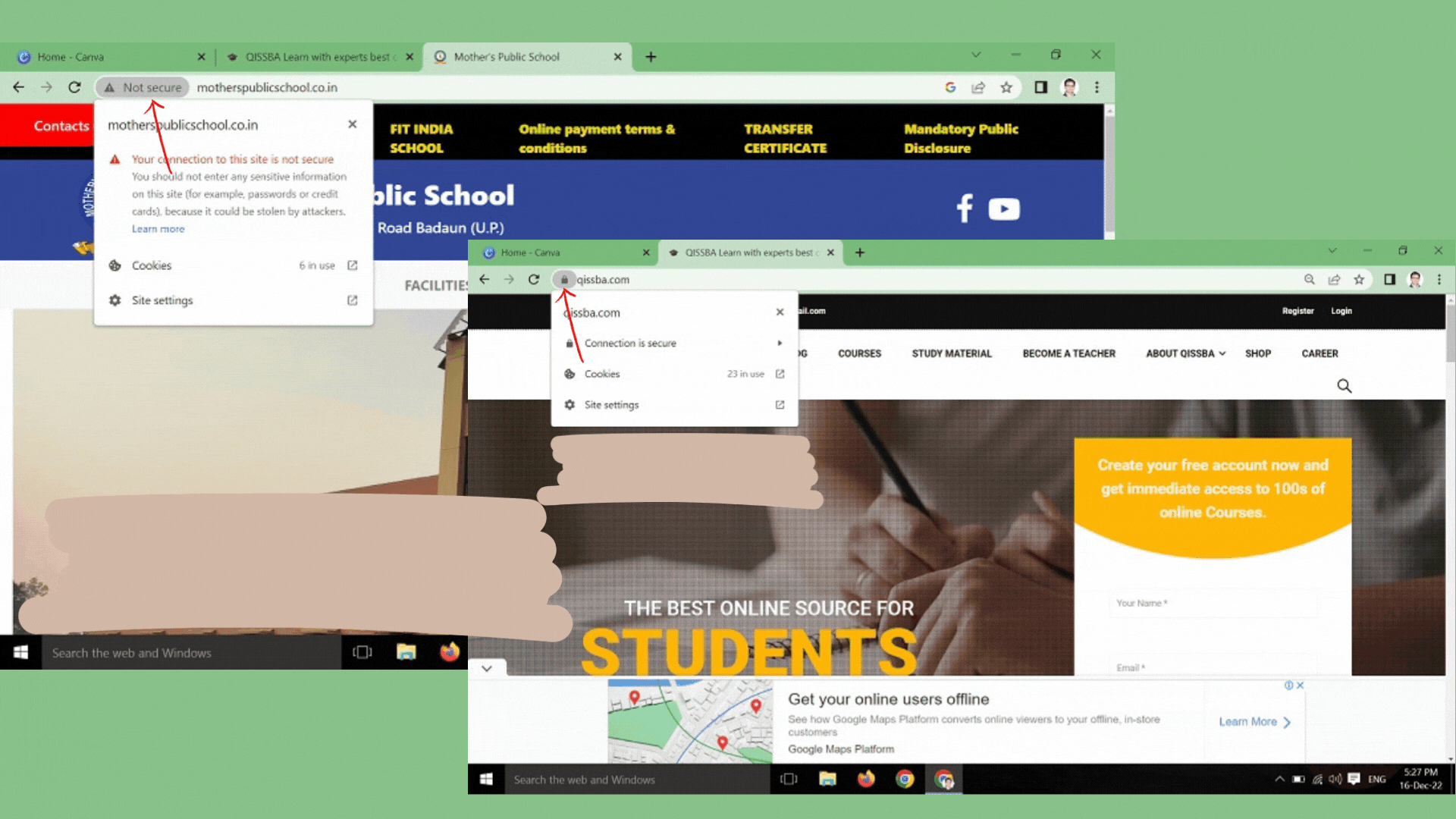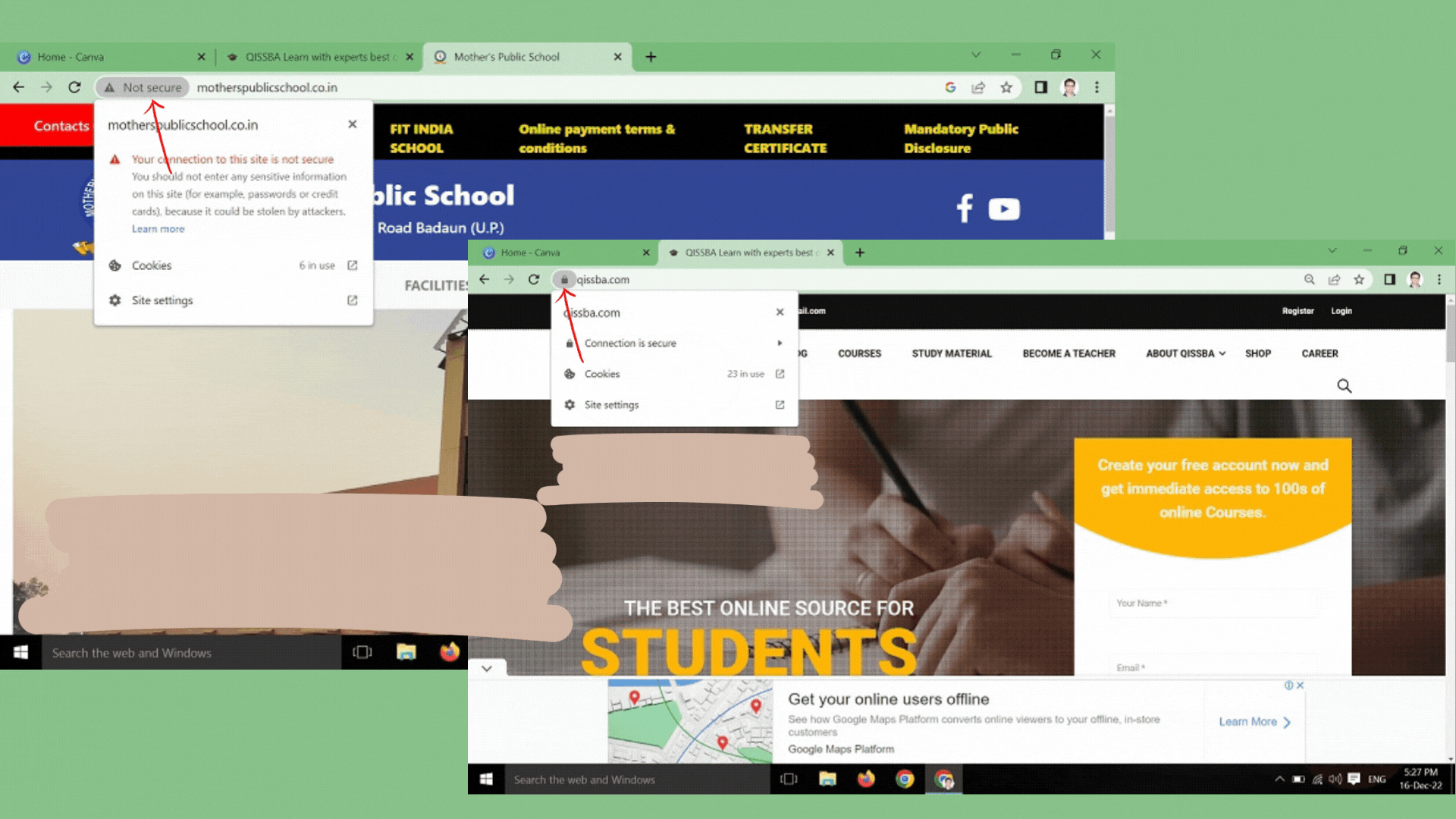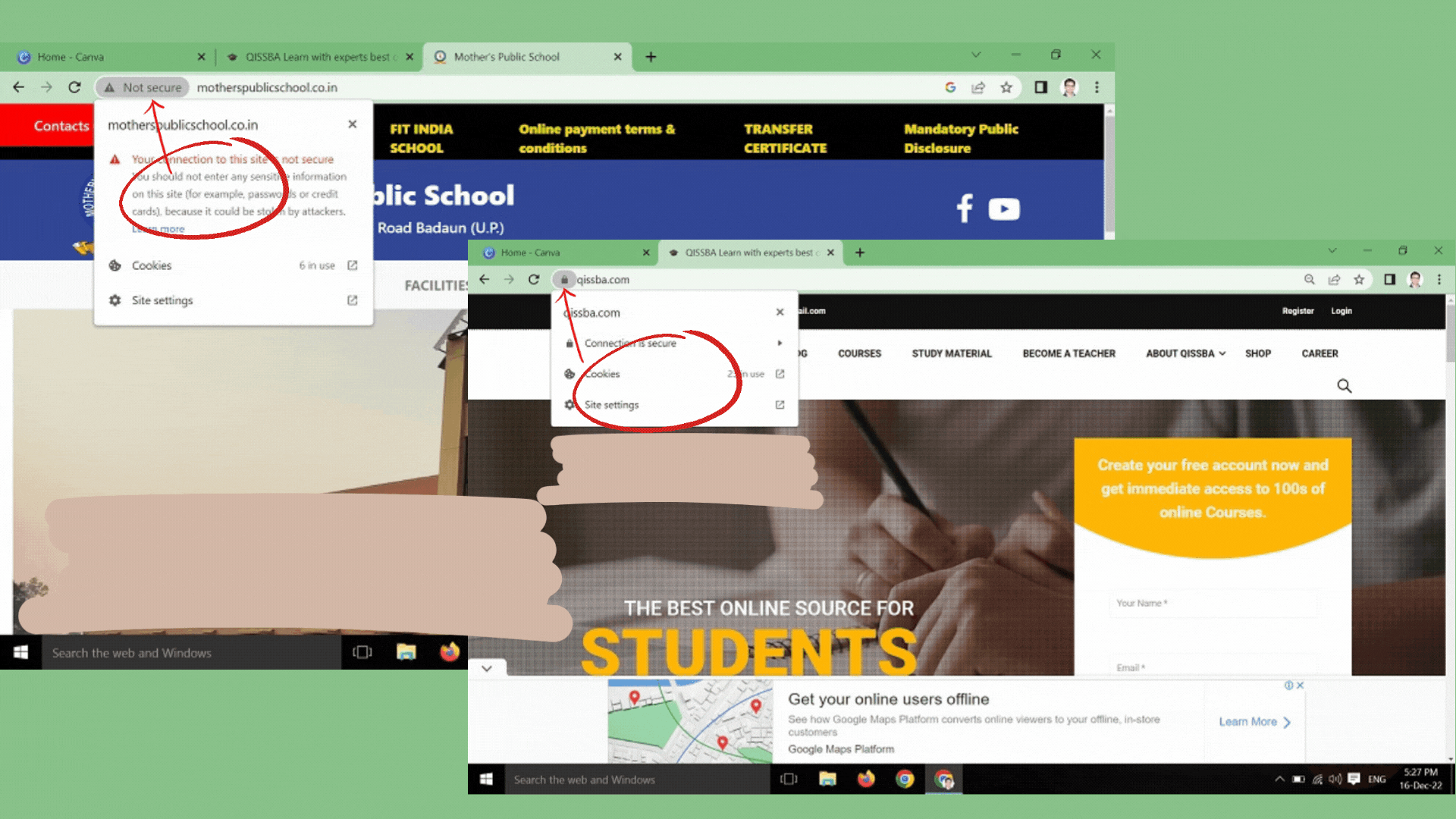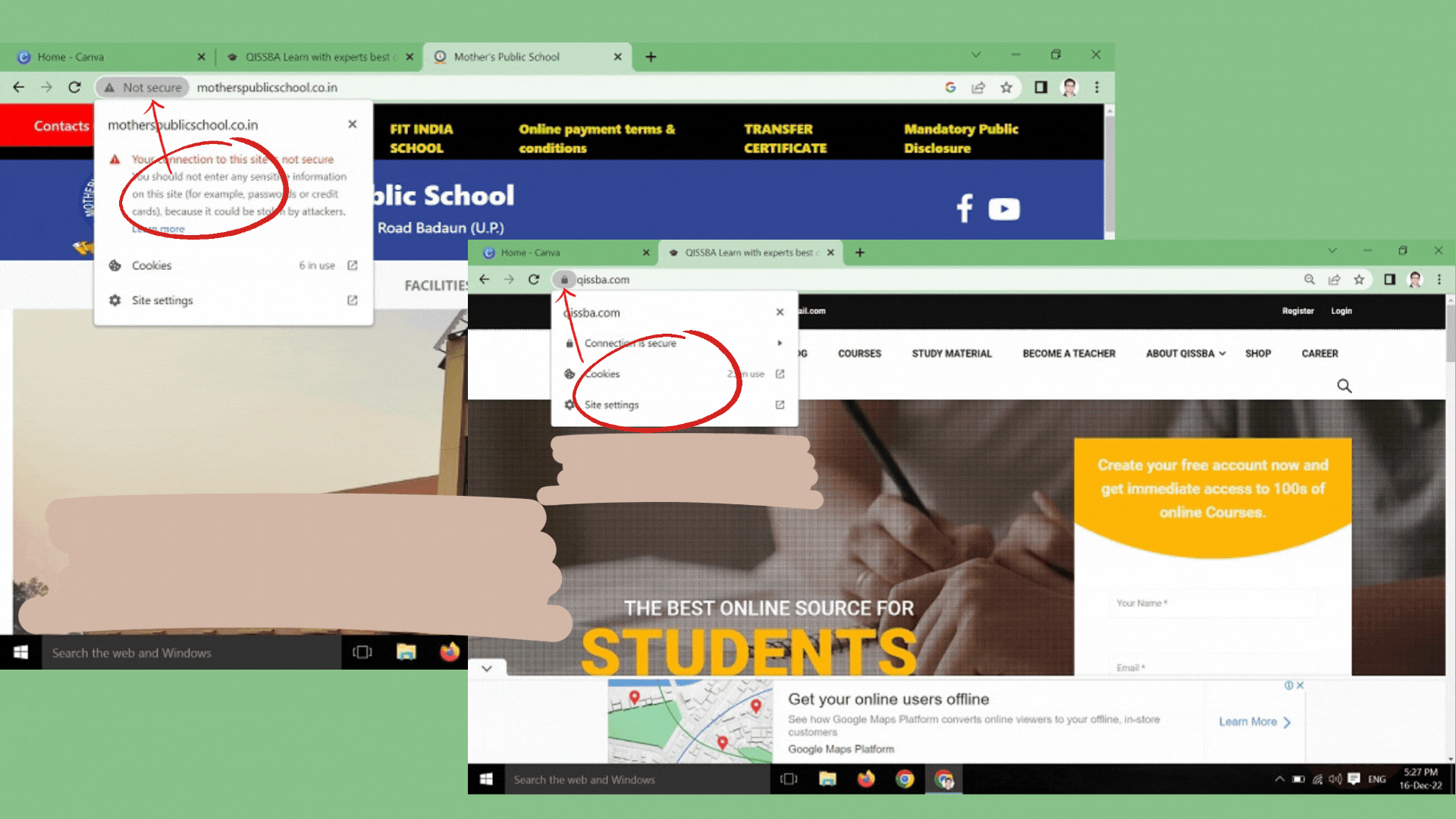
Only download files from reputable websites by looking for signs, such as a privacy statement, full contact information, and SSL encryption of sensitive information, typically indicated by a padlock in the lower-right corner of your web browser.- Be careful with email.
Email is a very convenient and useful communication method; however, it is also used by hackers, spammers, and criminals to get what they want. Follow these guidelines: - Don’t download or open unsolicited email attachments.
- Watch for Phishing scams. Be careful of an email that asks you to verify your personal details. Don’t click on any link provided in the email. Rather type the address of concerned bank or site in browser and find out the truth.
- Check for security alerts.
- Review your web browser settings regularly e.g., disable running of scripts and cookies etc.
- Disconnect from the Internet when you’ re away.
- Be careful with email.
- Disable Cookies, if possible
If you are particular about the safety of your personal information, then you may disable cookies on your browser. For this, just click the Help menu of your browser and search for how to block cookies.
Solutions to Spam, Eavesdropping
Spam has become the bane of the Internet, and still there is no real solution in sight. Spam 1s usually detined as “unsolicited e-mail” and resembles the flyers from stores that clog your newspapers each morning, but it’s much more than that. Protecting yourself against spam involves the following safeguards:
Active Protection
- Use Anti-Spam software.
Following are two of main methods used by anti-spam software to get rid of spam:
(i) Sender filtering. This method allows only messages from your approved sender list to reach
your inbox- all other mail is quarantined for later review. Sender filtering is done on the basis of digital certificates and digital signatures.
- Digital Certificates, specially formatted digital information issued to website, are used to verify the identity of the message sender to the recipient. Digital certificates are issued by a certificate authority (CA) that is trusted by both the sender and recipient.
- Digital signatures are a way of authenticating the identity of creators or producers of digital information. A digital signature is like a handwritten signature and can have the same legal authority in certain situations, such as buying and selling online or signing legal contracts.
(ii) Keyword filtering. This method filters out email messages that contain certain keywords or phrases, which are defined by you or others.
Preventive Measures
- Keep your email address private.
Be careful whom you give your email address to. Before giving your address out on an online form, check if there is a website privacy policy. This policy typically informs you of how they handle your personal information. Signing up for free offers seen online or by email may dramatically increase your chances of receiving spam messages. - Use encrypted connection always especially it you have to provide sensitive information. Encrypted connections are made possible through protocols like Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) and Secure Shell (SSH) and offer better security to data being transmitted.
- Install personal firewall on computers connected to the Internet so as to keep a check on incoming and outgoing information and connections.
- Always avoid conducting online transactions or using online banking services on public networks or public Internet facilities (e.g., public Wi-Fi).
- Install protection software such as Internet security software that also provides intrusion prevention system to detect and prevent further attacks by eavesdroppers.
Solutions to PC Intrusion
The combination of identification, authentication and authorization can control access to a system. This combination is very useful especially in network security. Various techniques used for network security are given below:
Active Protection
Authorization
Asking the user a legal login-id performs authorization. If the user is able to provide a legal login-id, he/she is considered an authorized user.
Authentication
Authentication is also termed as password-protection as the authorized user is asked to provide a valid password, and if he/she is able to do this, he/she is considered to be an authentic user.
Firewall
A system designed to prevent unauthorized access to or from a private network is called Firewall. Firewalls are a mechanism to prevent unauthorized Internet users from accessing private networks connected to the Internet, especially intranets.
Preventive Measures
Use proper File access permissions when sharing files on the Internet.
File access permissions refer to privileges that allow a user to read, write or execute a file.
- If a user has Read permission for a file, he/she can view and read the file.
- If a user has Write permission for a file, he/she can edit and write into the file.
- If a user has Execute permission for a file, he/she can execute the file.
File permissions are given for three sets of users: owner, group and others.
Owner -the user who has created the file.
Group – the group of users who are working with the owner as a group.
Others-all other users.
So, you can decide upon the file permissions, so that an unknown user does not get write or execute permissions at all.
Disconnect from the Internet when away
Using “always on” internet connections such cable and DSL increases your chances of some infections and intrusions as your PC is always connected to the Internet. This doesn’t mean you should switch back to dial-up Internet however, you may want to disconnect from your “always on’” connection when you don’t plan on using it for a long period of time.
Solutions to Phishing and Pharming Attack
Phishing is the fishing for confidential information. It is a scam that encompasses fraudulently obtaining and using an individual’s personal or financial information. Pharming refers to the redirection of an individual to an illegitimate Web site through technical means. To counter these evil twins is a task where you need alertness and carefulness. You can use following safeguards to counter these attacks:
Active Protection
If, somehow, you have become a victim of these attacks, then follow these guidelines:
Take the computer offline
Disconnecting from the internet reduces the probability of infecting other devices in the same network with malware.
Backup all files on the hard drive
If backing up data is routinely done, it is only necessary to backup new files. Focus on capturing all sensitive data and irreplaceable files such as videos and family photos.
List the information given to phishing scammers
Depending on what was leaked, one may need to change passwords, or cancel credit cards etc. BUT here you need to be very very cautious. DO NOT USE THE COMPROMISED COMPUTER TO CONTACT AGENCIES because using the same device may open users to the risk ofa freshly installed keylogger, which can record the new password as well.
Run anti-virus software.
Do not trust free anti-virus programs. They can be malware in disguise. It is advised to take the infected computer to a professional who specializes in malware removal.
Contact credit agencies to report any possibilities of identity theft
Reach out to credit bureaus that operate and manage the credit cards, as it will sound the alarm to potential creditors.
Preventive Measures
Phishing, and to a lesser extent, pharming, rely on tricking users rather than advanced technology, the best way to handle these threats is through vigilance.
- Don’t open emails from unknown sources or click on links embedded in suspect messages.
- Check the security guidelines of websites such as PayPal so that you can distinguish between legitimate and bogus emails.
- Also, rather than clicking on the link embedded in an email, you can type the general link in your web browser (e.g. http://www.paypal.com).
- Most important, when in doubt, do not click.
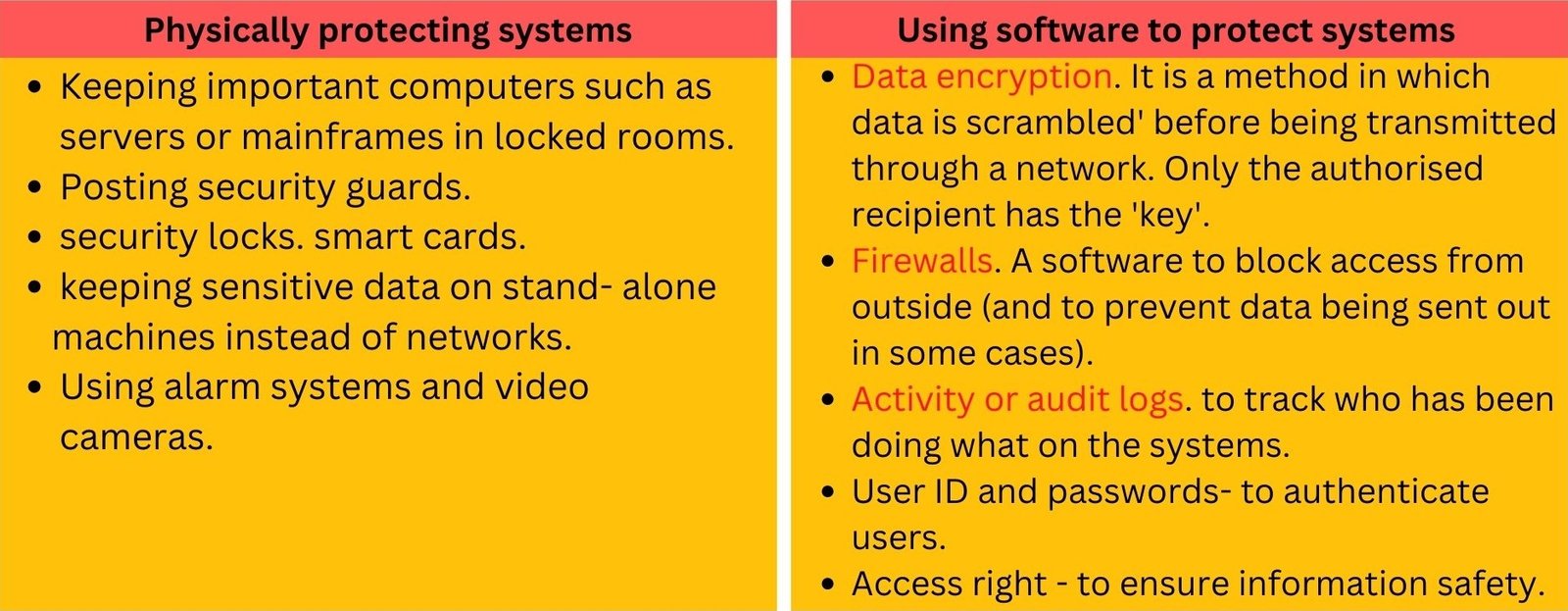
Firewall – An Important Solution for Computer Security
An Internet firewall is a device or software that is designed to protect your computer from data and viruses that you do not want. A firewall is so called because of the real firewalls used to secure buildings. A physical firewall is a set of doors that closes in a building so as to contain a fire to one area, preventing the entire building from being destroyed. Likewise an Internet firewall is designed to shut off access to your operating system or to other computers that are connected to your network.
Firewalls can be implemented in two forms:
1. Software Firewall
A software firewall is a special type of computer software running on a computer. it protects your computer from outside attempts to control or gain access, and, depending on your choice of software firewall, it could also provide protection against the most common Trojan programs or e-mail worms.
2. Hardware Firewall
It is physical piece of equipment designed to perform firewall duties. A hardware firewall may actually be another computer or a dedicated piece of equipment which serve as a firewall. Hardware firewalls can be effective with little or no configuration, and they can protect every machine on a local network.
Firewalls keep out malevolent hackers and people who intended to do damage and take over other peoples Servers. Firewalls really serve no other purpose. Firewalls seek to limit the access to a server or computer an let i only the people who need to be there.


