Modules in Python | CBSE Class 11 | Computer Science
Dear Class 11th STUDENTS, ! Welcome to this tutorial of Introduction to Modules in Python from your CBSE class 11 of Computer Science Syllabus .
In this tutorial, we shall be learning our chapter-12: Introduction to Modules in Python from Unit 2: Programming and Computational Thinking (PCT-1) as CBSE BOARD suggested to learn about computer system and its organisation to complete this section.
After going through this tutorial, you will be able to understand the following topics from your latest syllabus 2025-26.
Unit 2: Programming and Computational Thinking (PCT-1)
Chapter 12 : Introduction to Modules in Python
- Importing module using ‘import ’ and using from statement,
- Importing math module (pi, e, sqrt(), ceil(), floor(), pow(), fabs(), sin(), cos(), tan()); random module (random(), randint(), randrange()), statistics module (mean(), median(), mode()).
I advice you to check the latest syllabus given by CBSE Board at its Official website: www.cbseacademic.nic.in
Also, in this tutorial we will covers all necessary topics/concepts required to complete your exams preparations in CBSE classes 11th.
Also, you can Sign Up our free Computer Science Courses for classes 11th and 12th.

NOTE:
- We are also giving some important Questions & Answers for better understanding as well as preparation for your examinations.
- You may also download PDF file of this tutorial from our SHOP for free.
- For your ease and more understanding, we are also giving the video explanation class of each and every topic individually, so that you may clear your topics and get success in your examinations.

What is a Module in Python?
The act of portioning a program into individual components (known as modules) is called modularity. A module is a separate unit in itself. the justification for portioning a program is that
- It reduces its complexity to some degree and
- It creates a number of well-defined, documented boundaries within the program.
Another useful feature of having modules, is that its contents can be reused in other programs, without having to rewrite or recreate them.
For example, if someone has created a module, is that its contents can be reused in other programs, without having to rewrite or recreate them.
For example, if someone has created a module say ‘play audio’ to play different audio format, coming from different sources, e.g., mp3player, FM-radio player, DVD player etc. now, while writing a different program, is someone wants to incorporate FM-radio into it, he need not re-write the code for it. Rather, he can use the FM-radio functionality from play audio module. Isn’t that amazing? re-usage without any re-work – well, that’s the beauty of modules.
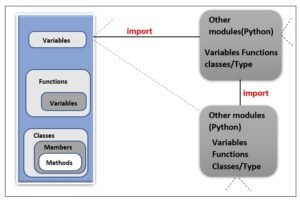
structure of a python module
A python module can contain much more than just function. A python module is anormal python file (. pyfile) containing one or more of the following objects related to a particular task

So, we can say that the module ‘XYZ’ means it is file ‘XYZ.py’.
Python comes loaded with some predefined module that you can use and you can even create your own modules. The python modules that come preloaded with python are called standard library modules. You have worked with one standard library module math earlier and in this tutorial, you shall also learn wo work with another standard library module: random module.
Following figure shows the general composition / structure of a python module.
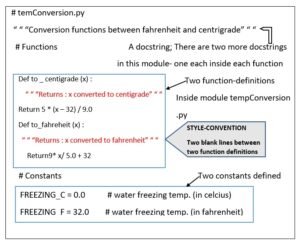
Let’s have a look at an example module. Namely temp conversion to figure 4.2.
(Please note, it is not form python’s standard library: it is a user created module, shown here for your understanding purposes).
Using of import < module > command
When you issue import < module> command, internally following things take place:
- The code of imported module is interpreted and executed 4.
- Defined functions and variables created in the nodule are now available to the program that imported module.
- For imported module, a new namespace is setup with the same name as that of the module
For instance, you imported module my Mod in your program. Now all the objects of module my Mod would be referred as my mod. <object- name>, e.g., if my Mod has a function defined as checksum ( ), then it would be referred to as my mod. Checksum ( ) In your program
Using of from <module> import <object> command
When you issue from <module>import <object> command, internally following things take place:
- The code of imported module is interpreted and executed 4.
- Only the asked functions and variables from the module are made available to the program.
- No new namespace is crated, the imported definition is just added in the current namespace
Difference Between import Module and From Module Import Object
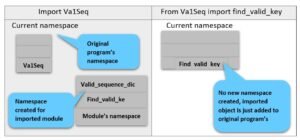
That means if your program already has a variable with the same name as the one imported via module, then the variable in your program will hide imported member with same name because there cannot be two variables with the same name in one namespace
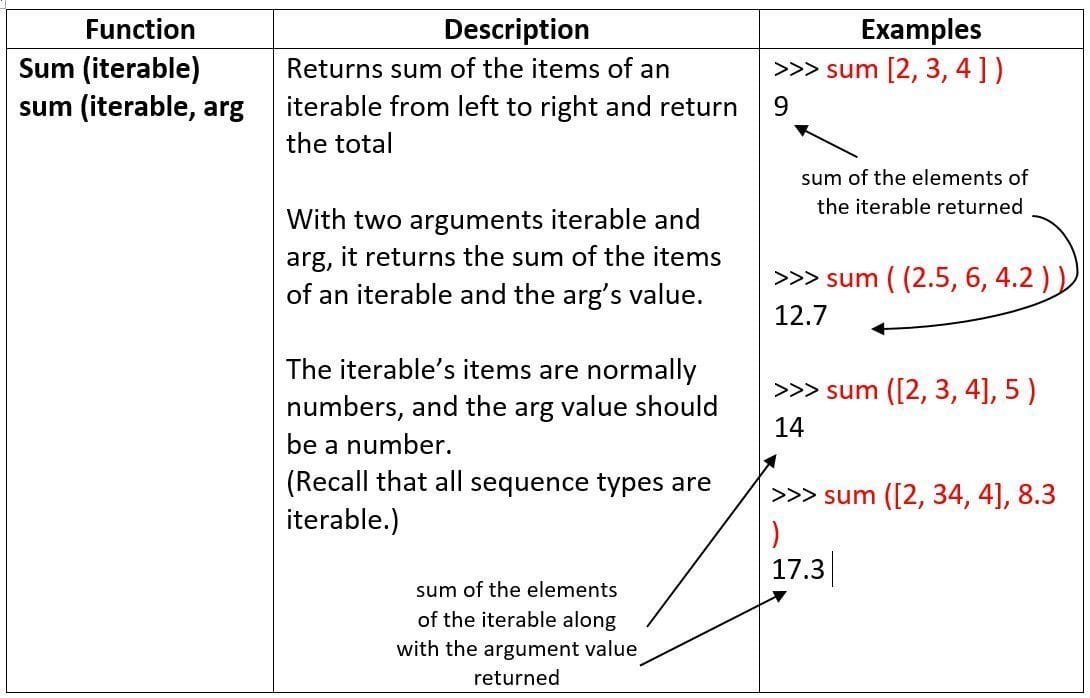
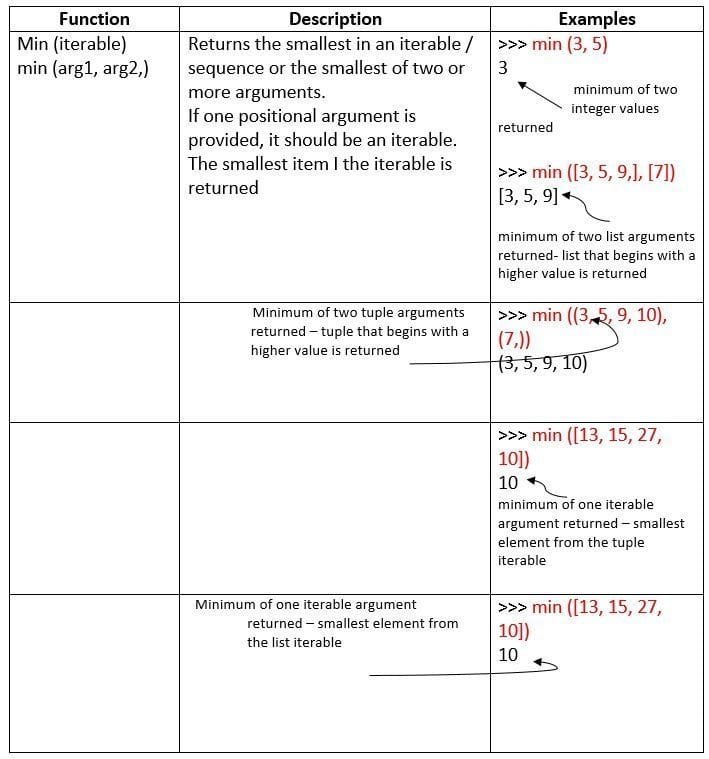
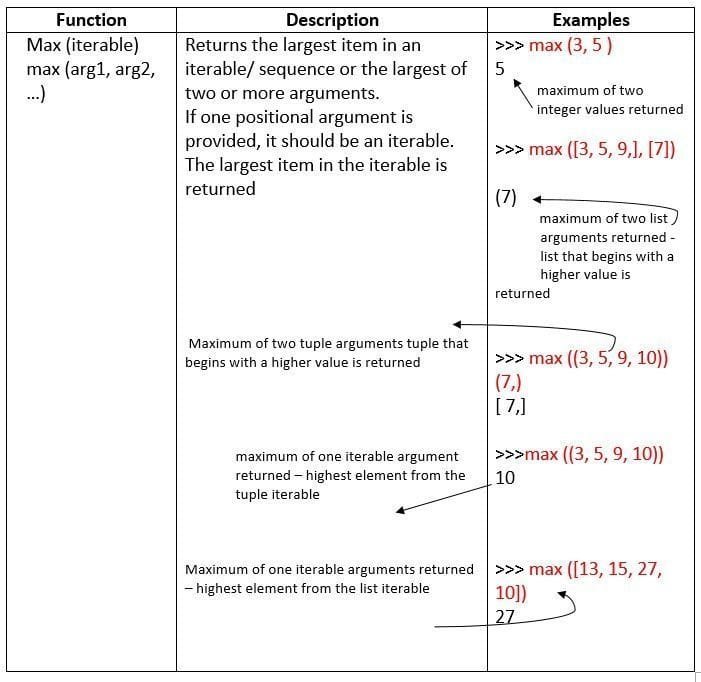
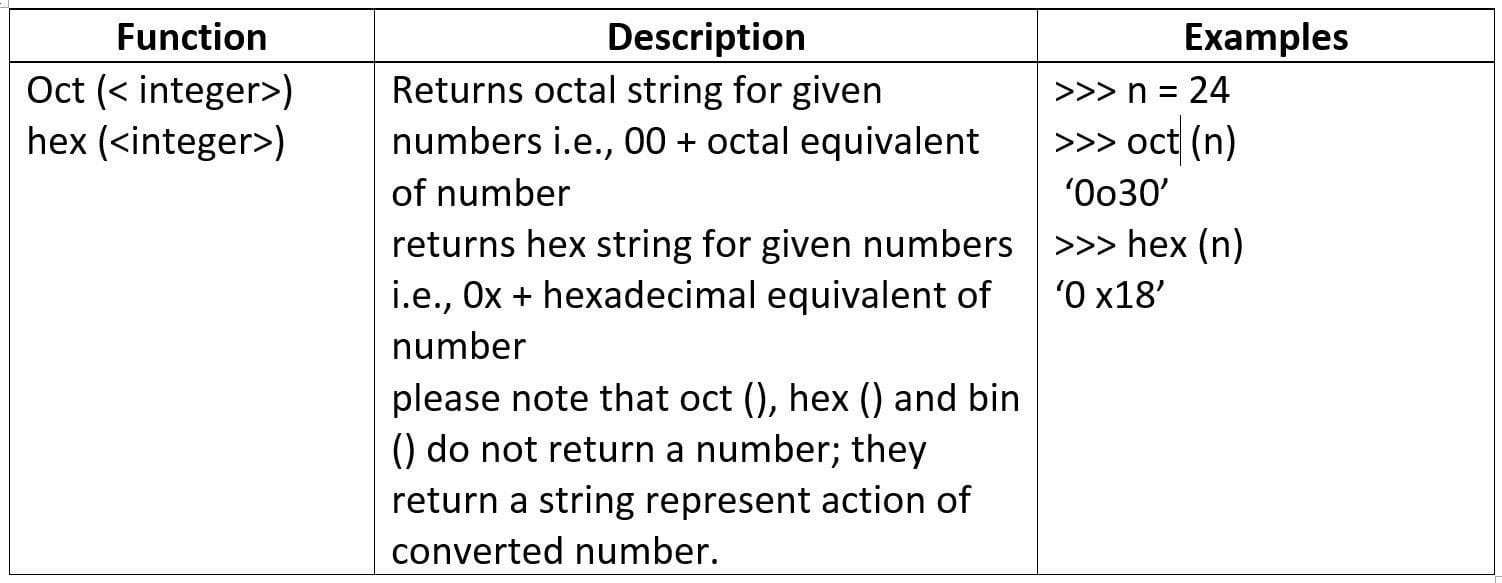
Let’s us now talk about some more built in mathematical functions.
Math Library Functions
Python’s standard library provides module namely math for math related functions that work with all number types except for complex numbers.
In order to work with functions of math module, you need to first import it to your program by giving statement as follows as the top line of your Python script:
import math
Then you can use math library’s functions as math. <function-name>
Table 1.2 Some Mathematical Functions in math Module
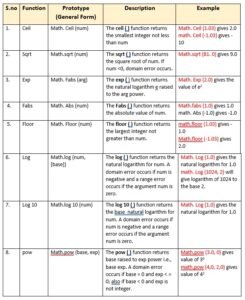
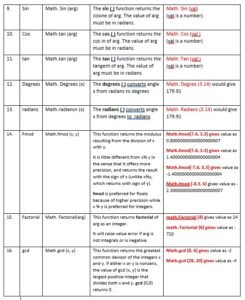
some useful built-in mathematical functions