
Digital Society and Netizen | CBSE Class 11 | Computer Science
Dear Class 11th STUDENTS, !
Welcome to this tutorial of Digital Society and Netizen from your CBSE class 11 of Computer Science Syllabus .
In this tutorial, we shall be learning our chapter-2: Digital Society and Netizen from Unit 3: Society, Law and Ethics (SLE-1)- Cyber safety as CBSE BOARD suggested to learn about computer system and its organization to complete this section.
Unit 3: Society, Law and Ethics (SLE-1)- Cyber safety
Chapter 2 : Digital Society and Netizen
- What is a Digital Society?
- What is a Netizen?
- What are Net Etiquettes?
- Communication etiquettes
- Types of Communication & Their Etiquettes
- Digital / Online Communication Etiquettes
- Golden Rules of Communication Etiquette
- Etiquette in Different Cultures
- What is Social Media Etiquette?
- Technology and society
I advice you to check the latest syllabus given by CBSE Board at its Official website: www.cbseacademic.nic.in
Also, in this tutorial we will covers all necessary topics/concepts required to complete your exams preparations in CBSE classes 11th.
Also, you can Sign Up our free Computer Science Courses for classes 11th and 12th.

NOTE:
- We are also giving some important Questions & Answers for better understanding as well as preparation for your examinations.
- You may also download PDF file of this tutorial from our SHOP for free.
- For your ease and more understanding, we are also giving the video explanation class of each and every topic individually, so that you may clear your topics and get success in your examinations.

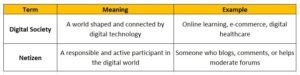
What is a Digital Society?
A digital society is a community or population that relies heavily on digital technology for everyday activities—communication, education, work, shopping, entertainment, and government services.
Key Features:
- Widespread internet access
- Smart devices like phones, tablets, and wearables
- Digital services (online banking, e-learning, e-governance)
- Data-driven decisions using AI, big data, etc.
- Remote communication & collaboration
Example:
Estonia is considered a highly digital society—citizens can vote, pay taxes, and access healthcare entirely online.
What is a Netizen?
A Netizen (internet + citizen) is someone who actively participates in the online world. They’re not just users—they engage, contribute, and behave responsibly on the internet.
Characteristics of a Good Netizen:
- Respectful online behavior
- Sharing useful content
- Following digital ethics and laws
- Helping others stay safe online
- Fighting misinformation or cyberbullying
Example:
Someone who contributes to online discussions, reports harmful content, and educates others about digital safety is a responsible netizen.
What are Net Etiquettes?
Net etiquettes (or netiquette) are the rules and guidelines for polite, respectful, and responsible behavior when communicating and interacting online. Just like we follow manners in real life, netiquette helps create a positive and safe digital environment.
Key Net etiquette Guidelines:
1. Be Respectful
- Treat others kindly, even if you disagree.
- Avoid hate speech, insults, or offensive language.
2. Think Before You Post
- Once something is online, it’s hard to delete.
- Ask: Is this true? Helpful? Kind? Necessary?
3. Use Proper Language and Tone
- Avoid using ALL CAPS (it’s like shouting).
- Use clear and polite language.
4. Respect Others’ Privacy
- Don’t share someone’s personal information without permission.
- Avoid taking screenshots or forwarding private messages.
5. Don’t Spam
- Avoid sending repeated or irrelevant messages or emails.
- Don’t flood group chats with off-topic content.
6. Give Credit
- Always credit sources when you use images, quotes, or ideas.
- Don’t plagiarize.
7. Be Careful with Humor and Sarcasm
Tone can be misunderstood online—what’s funny to you might seem rude to others.
8. Follow the Rules of the Platform
- Every website or platform has its own rules—follow them.
- Report harmful content rather than joining in.
9. Use Emojis Wisely
Emojis can help express tone but don’t overuse them.
10. Be Inclusive and Open-Minded
- Respect different cultures, beliefs, and opinions.
- Avoid making assumptions about others.
Example:
If you’re commenting on a classmate’s post in an online classroom:
❌ “This is dumb. You don’t know anything.”
✅ “I see your point, but I think there might be another way to look at it. What do you think about this?”
Communication etiquettes
refer to the set of polite and respectful behaviors that people follow while exchanging messages, whether in person, over the phone, or online. These etiquettes help ensure that conversations are clear, effective, and respectful.
Types of Communication & Their Etiquettes
1. Verbal Communication Etiquettes
These apply when you’re speaking face-to-face or over the phone.
✅ Do:
- Speak clearly and at a moderate pace.
- Use polite language (e.g., please, thank you, excuse me).
- Listen actively without interrupting.
- Use respectful tone and body language.
❌ Don’t:
- Interrupt while someone else is talking.
- Use slang or offensive words in formal settings.
- Shout or speak too softly.
🧠 Example:
In a team meeting, saying “I see your point. Can I share a different idea?” is polite and respectful.
Non-verbal Communication Etiquettes
This includes body language, eye contact, gestures, and facial expressions.
✅ Do:
- Maintain good eye contact.
- Nod occasionally to show attentiveness.
- Keep an open posture.
❌ Don’t:
- Cross your arms or avoid eye contact—it may seem like disinterest or disrespect.
- Use distracting gestures.
🧠 Example:
Smiling when greeting someone creates a welcoming atmosphere.
Written Communication Etiquettes
This includes emails, messages, letters, reports, or texts.
✅ Do:
- Use correct grammar and punctuation.
- Be concise and to the point.
- Start with a greeting and end with a closing remark.
- Use a respectful tone, even in disagreements.
❌ Don’t:
- Use all caps (it feels like shouting).
- Send messages without a subject or signature (in emails).
- Use emojis in formal messages.
🧠 Example (Email):
Subject: Request for Project Extension
Dear Sir,
I hope this message finds you well. I would like to request an extension on the project deadline due to unforeseen circumstances…
Sincerely,
Qissba Khan
Digital / Online Communication Etiquettes
Includes messaging apps, social media, video calls, etc.
✅ Do:
- Mute your mic when not speaking in a meeting.
- Use professional language on work-related platforms.
- Respect people’s time and privacy.
❌ Don’t:
- Spam with too many messages.
- Use offensive language or make jokes that may be misunderstood.
🧠 Example:
Before adding someone to a group chat, ask their permission.
Golden Rules of Communication Etiquette
| Rule | Description |
|---|---|
| Be respectful | Always treat others with kindness, even when you disagree. |
| Be clear | Speak or write in a way that’s easy to understand. |
| Be timely | Respond promptly, especially in professional settings. |
| Be attentive | Listen more than you speak. |
| Be open-minded | Accept feedback and different opinions without reacting rudely. |
Etiquette in Different Cultures
| Culture | Common Etiquette |
|---|---|
| Japan | Bowing to show respect; avoid direct confrontation. |
| USA | Firm handshakes; maintain eye contact. |
| India | Greet with “Namaste” or a polite “Hello”; respect elders. |
What is Social Media Etiquette?
It’s a set of unwritten rules that guide how we post, comment, share, like, and interact online. Practicing good etiquette on social media helps:
- Build a positive online image.
- Avoid misunderstandings or conflicts.
- Maintain relationships—both personal and professional.
- Stay safe and respectful in the digital world.
Basic Social Media Etiquette Rules
1. ✅ Think Before You Post
Ask yourself:
- Is this appropriate?
- Could this offend someone?
- Will I regret this later?
🧠 Example: Avoid sharing personal fights, offensive jokes, or political rants in public posts.
Technology and society
ICT s are general purpose technologies, i.e., technologies whose value and impact arise primarily from their use in other economic and social sectors. Three capabilities are especially important for economic and social development.
Information and Communication Technologies:
- Enable greater efficiency in economic and social processes;
- Enhance the effectiveness of cooperation between different stakeholders; and
- Increase the volume and range of information available to people, businesses and governments.
Systemic impacts which ICTs have had on the development of economies, societies and culture, include:
Economic impacts: include the globalization of production in goods and services, changes in international trade and distribution networks, changes in patterns of consumption, the virtualization of some products and behaviors, and the growing importance of the ICT sector within the world and national economies.
Social Impacts: include mass market access to an enormously increased range of information resources, enhanced freedom of expression and association, new patterns of work and human settlement, changed in the relationships between government, citizen and the state, and between citizens, and associated challenges to traditional ideas of privacy and individuality.
Economic Benefits
The impact of ICT on the economic sector has a positive multiplier effect on the business World. Some major benefits include:
Secure Transactions:
Banks and similar institutions could be said to be the sector that have benefited the most from latest developments in ICCT. Fund transfer can now be made in a matter of seconds within a locality and to the most parts of the world with a greater security than ever.
Ease and Availability:
One doesn’t need to stand in long queues for fund withdrawal; with the use of the ATM card and Internet banking, the banking transactions can be carried out at any time of the day within the scope of transactions allowed. Such transactions could even include payment of bills such as electricity, water rates etc.
Net Banking:
With online or Internet banking a lost s of payments and buying can be done online via one’s bank account at the convenience of one’s home or office. The life wire of any business is fund availability and its timeliness and net banking ensure both.
Global Market:
With ICT, now the market is entire globe. A small business in a small town can think of reaching to a buyer in any part of the world. And buyer’s access is not just limited to his own market, (s) he can have access to the all world market, courtesy Internet and ICT.


