Mobile System Organization | CBSE Class 12
Introduction
Mobile system organization refers to the software system that allows mobile devices to run applications and programs, and the interface between the device’s hardware and software. Mobile system organization is also called as Mobile Operating System (Mobile OS).
Mobile operating system (OS)
Mobile System Organization
Modern mobile system are tiny computers in your hand. Although they have less computing power compared to their bigger versions, they handle diverse type of applications such as making calls through radio signals, offering camera utilities, handling touch sensitive screen, display audio/video/graphical content but having little battery-based power etc.
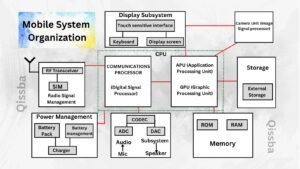
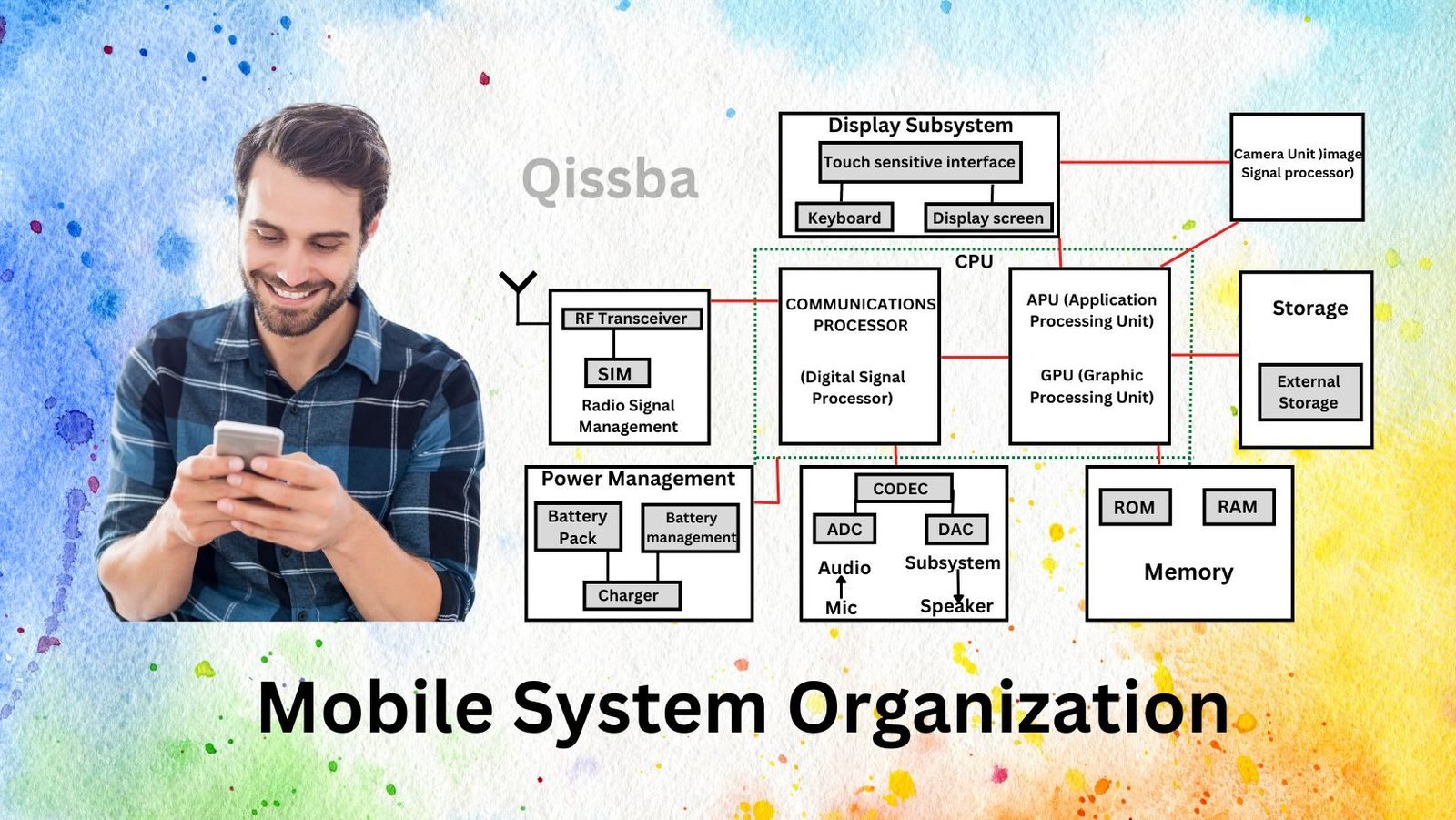
Thus, the system organization of a mobile system has components to handle all these. The block diagram of a mobile system is as shown here.
Let us talk about these functional components of a mobile system one by one.
A mobile system’s these CPU handle diverse types of applications but has a little power compared to computers as mobile systems run on battery power.
Mobile Processor (Mobile CPU)
This is the brain of a smartphone. The CPU receives commands, makes instant calculations, plays audio/video, stores information and sends signals throughout the device.
The CPU of a mobile system has majorly two sub-processor2 types:
- Communications Processing Unit
- Applications Processing Unit (APU)
- Communications Processing Unit. [mobile System 1/0 Unit] This subsystem is responsible for making and receiving phone calls on a mobile handset. It has a digital signal processor that helps it work with RF Transceiver and the Audio subsystem.
- Radio Signal Management Unit is responsible for connecting SIM (which provides a type of modern) to the base stations through radio signals. (3G/LTE/4G BASED cellular network).
- Applications Processing Unit (APU). The subsystem is responsible for governing, controlling all types of operations taking place on a mobile system by running various type of mobile application (apps).
Display Subsystem
This subsystem is responsible for providing display facilities, touch sensitive interface and touch sensitive keyboards.
Camera Subsystem
This subunit is designed to deliver a tightly bound image processing package and enable an improved overall picture and video experience. It has an integrated image Signal Processor ensures things like instant image capture, high-resolution support, image stabilization, and other image enhancements.
Mobile System Memory
Like its other counterparts, a mobile system also needs memory to work. A mobile system’s memory is comprised of following two types of memories:
- RAM (Random Access Memory). It is the work memory of your mobile system. The installed mobile apps, when run, are first loaded in the RAM and then executed. These apps remain in the RAM after you are no longer using them and then they are shifted to background.
The more RAM you have on a smartphone, the better performance and faster the, phone will generally be. RAM does not store information once the device is turned off.
- ROM (Read Only memory). The ROM or Read Only Memory is a part of mobile system’s internal storage and it is not accessible for users to write on and is thus referred to as Read Only Memory. The ROM is basically Flash memory or technically EEPROM (electrically erasable and programmable read only memory).
This ROM part of a mobile. System internal storage is where operating system resides. It also has some preinstalled apps in this memory sections which cannot be deleted on users ‘end either. This is the reason why you don’t get full internal memory as advertised on the Box, because a part of it has been used to house operating system and other pre-installed apps.
Storage
The external storage of a mobile system is also called expandable storage. It comes in the form of SD cards, or micro-SD cards etc. It is the storage which can be removed easily by you and can be used for storing pictures, music, videos and the likes. To an extent, even the cloud storage can also be categorized as external storage.
Power Management Subsystem (Battery)
This subsystem is responsible for providing power to a mobile system. The mobile System work on limited power provided through an attached battery unit. This Subsystem has a battery management system that works with a battery charger and Provides power to the mobile system in required form.
Key Features of Mobile System OS
Some key functions of a mobile OS include:
- User interaction: Allowing users to process input from the screen, camera, or number pad
- Applications: Allowing users to download and install software
- Memory management: Allocating and de-allocating memory, and keeping track of which parts are being used by which programs
- Security: Protecting the device’s computer security
- Performance: Controlling the system’s performance
Popular Mobile System OS
Some popular mobile OSs include:
- Android: Built by Google, with a 71.67% market share on smartphones and other mobile devices
- iOS: Developed by Apple Inc., with a 27.73% market share on smartphones and other mobile devices
- Symbian OS: Developed by Nokia
- BlackBerry OS: Developed by BlackBerry
- Windows Mobile: A mobile OS
- FireOS: Developed by Amazon
EXAM TIME
———————————————————————————————————
Here are some answers to questions about
A mobile OS is a software platform that allows users to run apps and programs on their mobile devices. It acts as an interface between the device’s hardware and software, and usually starts when the device turns on.
Q2. What are some common mobile OSs?
Some common mobile OSs include:
- Android
- Apple iOS
- Bada
- Blackberry OS
- Windows Mobile OS
- Symbian OS
- Palm OS
- Web OS
- Harmony OS
Q3. How do mobile OSs compare to desktop OSs?
Mobile OSs are a combination of computer OS features and additional features for mobile use. They usually include a wireless modem and SIM tray for data and phone connection.
Q4. How do mobile OSs manage network connectivity?
Mobile OSs manage cellular and wireless network connectivity, as well as phone access.
Q5. What does a mobile OS typically display when a device starts up?
When a device starts up, a mobile OS usually displays a screen with icons or tiles that provide application access and show information.
Q6. Who created Android?
Google created the open-source Android mobile OS, which was first released in 2008.
Q7. What is the latest version of Android?
The latest version of Android is Android 15, which was released on September 3, 2024.


