
Cyber Crime | CBSE Class 11 | Computer Science
Dear Class 11th STUDENTS, !
Welcome to this tutorial of Cyber Security | Safety from your CBSE class 11 of Computer Science Syllabus .
In this tutorial, we shall be learning our chapter-5: Cyber Security | Safety from Unit 3: Society, Law and Ethics (SLE-1)- Cyber safety as CBSE BOARD suggested to learn about computer system and its organisation to complete this section.
After going through this tutorial, you will be able to understand the following topics from your latest syllabus 2025-26.
Unit 3: Society, Law and Ethics (SLE-1)- Cyber safety
Chapter 4 : Cyber Crime:
- Definition,
- Hacking,
- Eavesdropping,
- Phishing and fraud emails,
- Ransomware,
- Cyber trolls,
- Cyber bullying
I advice you to check the latest syllabus given by CBSE Board at its Official website: www.cbseacademic.nic.in
Also, in this tutorial we will covers all necessary topics/concepts required to complete your exams preparations in CBSE classes 11th.
Also, you can Sign Up our free Computer Science Courses for classes 11th and 12th.

NOTE:
- We are also giving some important Questions & Answers for better understanding as well as preparation for your examinations.
- You may also download PDF file of this tutorial from our SHOP for free.
- For your ease and more understanding, we are also giving the video explanation class of each and every topic individually, so that you may clear your topics and get success in your examinations.

Introduction to Cyber Crime
Cybercrime is any criminal offense that is facilitated by, or involves the use of, electronic communications or information system, including any electronic device, computer, or the internet. The term, cybercrime, is a general term that covers crimes like phishing, credit card frauds, illegal downloading, industrial espionage, child pornography, cyber bulling, cyber stalking, cyber terrorism, creation and/ or distribution of viruses, spam and so on.
Information Theft:
While working online, you often enter and create information related to you. You often enter information related to payments and even about your home address etc. while shopping. This information must be safe and must not fall into wrong hands. One should be careful while working online as there are many ways through which thieves can obtain your personal information:
Hacking
In cyber security, hacking refers to the unauthorized access and control of digital devices, systems, or networks, often by exploiting vulnerabilities to steal data, disrupt operations, or cause harm. It involves using technical skills and knowledge to bypass security measures and gain access to information or functionality without permission
Eavesdropping
Eavesdropping is a passive attack in which an attacker gains access to the communication-medium through which some communication is taking place and then listens to the communication and gets information about the content of the message.
Eavesdropping can be carried out through all communication devices and media of today- telephone systems, emails, instant messaging, other Internet services (e.g., chat rooms, social networking websites etc.), mobile devices etc. Eavesdropping activities do not affect normal operation of transmission and communication; thus both the sender and the recipient can hardly notice that the data has been stolen, intercepted or defaced.
For example, while sending emails, if the email message is not encrypted and digital signature has not been used, then the attacker can exploit these security loopholes. Because of these security lapses, the attacker can launch a Man-in-the-Middle attack on the network and intercept the message being transmitted. The attacker can then deface the message and send it to the recipient.
The recipient is then deceived into believing the defaced message is the real message and may act as per the defaced message and may provide personal or sensitive information.
Similarly sending or providing confidential information over insecure protocols like HTTP makes the information more prone to eavesdropping attack.
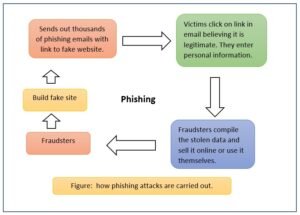
Phishing:
Phishing is the practice of attempting to acquire sensitive information from individuals over the internet, by means of deception. Information typically targeted by phishing schemes includes passwords, user-names, bank account information, and security numbers. The term ‘phishing’ is a play on ‘fishing’ – hackers use various forms of ‘bait’ in order to catch a victim.
It is the criminally fraudulent process of attempting to acquire sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, credit card information; account data etc. In phishing, an imposter uses an authentic looking email or web-site to trick recipients into giving out sensitive personal information. For instance, you may receive an email from your bank (which appears genuine to you) asking to update your information online by clicking at a specified link. Though it appears genuine, you may be taken to a fraudulent site where all your sensitive information is obtained and later used for cyber-crimes and frauds.
Fraud Emails
Email fraud is a type of scam that uses email to trick victims into revealing personal information or transferring funds to fraudulent accounts. For example, a criminal might send you an email with a logo from Google in the header pretending to be from Google asking for your password.
Email scammers use several strategies to bypass email defenses and trick users into divulging information or running malicious code. Some types of scam emails include a link to an attacker-controlled malicious website where the attacker collects sensitive data from victims.
To verify if the domain name (the bit after the @ symbol) matches the apparent sender of the email, the message is probably legitimate. By contrast, if the email comes from an address that isn’t affiliated with the apparent sender, it’s almost certainly a scam.
Social engineering / pretexting:
They pose as a legitimate business or government officials to obtain your personal information from financial institutions, telephone companies, and other sources.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malicious software (malware) that cybercriminals use to hold data or systems hostage, demanding a ransom payment for their release. It’s a serious cybersecurity threat that can severely disrupt operations and cause significant financial losses. Ransomware can be spread through various methods, including phishing emails, malicious downloads, and exploiting software vulnerabilities. Once executed, the ransomware can spread across a network, encrypting files and potentially locking users out of their systems. The attackers then demand a ransom, often using sophisticated methods to pressure victims into paying.
Cyber Trolls
Cyber troll refers to a person who purposely posts opposing-, sarcastic-, demeaning- or insulting-comments about something or someone with an aim of targeting a person online. The provocative messages posted this way are also called troll. So the word troll can refer to a person also who is doing it and it may refers to the derogatory comments posted by a troll. Trolling is a cybercrime and is closely related to cyber bullying. In fact, it is a form of cyber bullying.
Cyber Bullying
Cyberbullying occurs when someone uses the Internet, a cell phone, email, instant messaging, chat rooms, or social networks, such as Facebook, Twitter etc., to harass, demean, embarrass, or intimidate someone else. It is commonly a crime committed by teens too, as their growing access to electronic communication makes it possible to make fun of or ostracize others. The problem spreads like wildfire as the bully can hide behind the anonymity of a login identity, while encouraging other kids to join in the “fun” of harassing the victim. Cyberbullying is a crime, garnering such criminal charges as harassment, libel, assault, and even terrorism. In addition to criminal charges, cyberbullies may be held responsible for the damage they do in a civil lawsuit, where they may be ordered to pay for it.



